Figure 2. The functions of lncRNAs in pathogenesis and potential clinical applications in RCC.
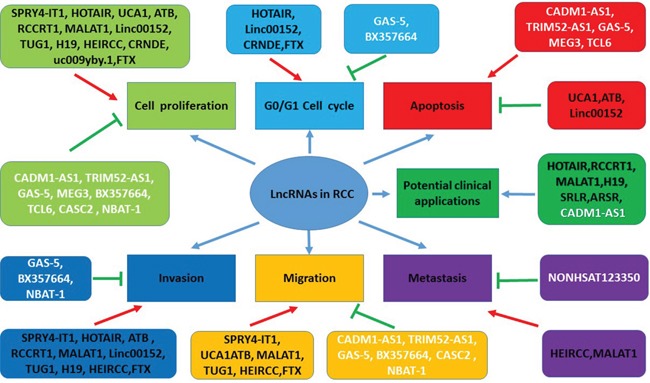
LncRNAs play multiple functions in the context of RCC, including regulating cell proliferation, cell cycle, apoptosis, invasion, migration, and metastasis in the forms of oncogenes or tumor suppressor genes. Some lncRNAs maybe serve as therapeutic targets and have the potential of the clinical application. Red arrows indicate promoted signaling pathways. Green arrows indicate inhibited signaling pathways. LncRNAs in black font indicate oncogenes. LncRNAs in white font indicate tumor suppressor genes. Some lncRNAs have multiple functions (for example, MALAT1 promotes cell proliferation, invasion, migration, and metastasis). Abbreviations: SPRY4-IT1: SPRY4 intronic transcript 1; HOTAIR: Hox transcript antisense intergenic RNA; UCA1: urothelial carcinoma-associated 1; lncRNA-ATB: lncRNA activated by TGF-β; MALAT1: metastasis-associated lung adenocarcinoma transcript 1; Linc00152: long intergenic noncoding RNA 152; TUG1: Taurine up-regulated gene 1; HEIRCC: high-expressed in renal cell carcinoma, lncRNA TCONS_00006756; CRNDE: colorectal neoplasia differentially expressed; CADM1-AS1: lncRNA cell adhesion molecule 1 antisense, lncRNA (RNA176206/ENST00000546273) located in the antisense direction of a coding exon of the cell adhesion molecule1 (CADM1); TRIM52-AS1: TRIM52 antisense RNA 1; GAS-5: growth arrest specific 5; MEG3: maternally expressed gene 3; TCL6: T-cell leukemia/lymphoma 6; CASC2: cancer susceptibility candidate 2; NBAT-1: neuroblastoma associated transcript 1; SRLR: sorafenib resistance-associated lncRNA in RCC; ARSR: lncRNA activated in RCC with sunitinib resistance, ENST00000424980.
