Figure 1. ZNF131 is a candidate GSC-lethal gene.
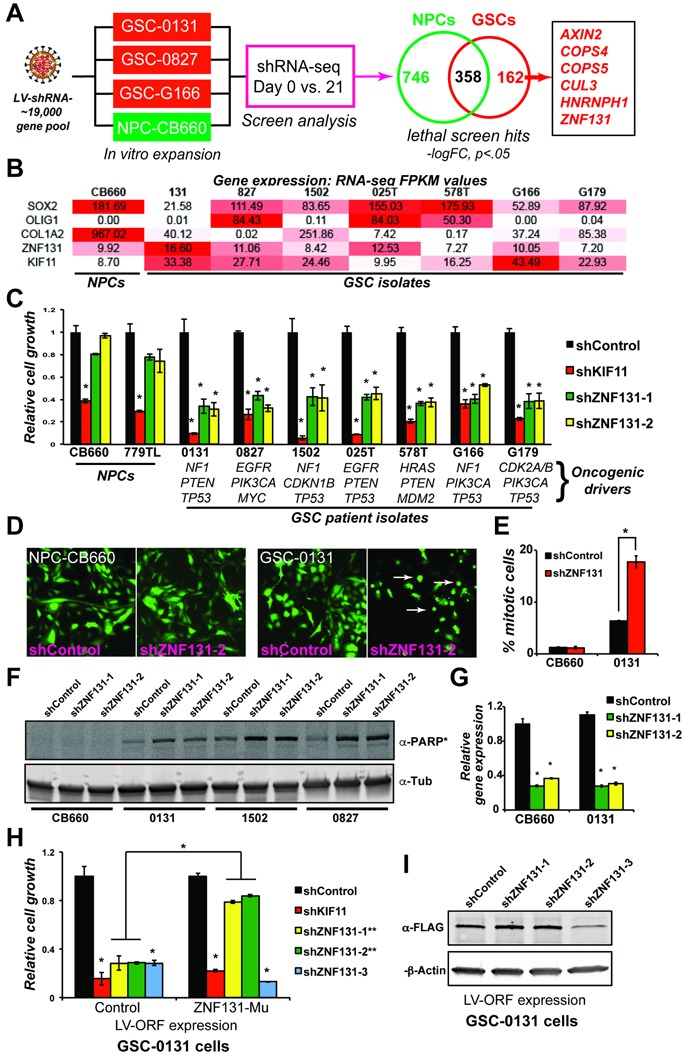
A. Overview of GSCs and NPCs shRNA screens that gave rise to ZNF131 as a candidate GSC-lethal gene. B. ZNF131 expression among NPC and GSC isolates. Values are from FPKM normalized RNA-seq data from self-renewing in vitro cultures. C. Short term growth assays showing differential viability requirement for ZNF131 among GSC and NPC isolates. Cell growth assays were performed 7 days after selection for LV-shRNAs in monolayer culture (n ≥ 3). D. Fluorescent micrographs of shRNA transduced cells (GFP+). Arrows show GSC cells displaying mitotic arrest phenotype observed with ZNF131 kd. E. Quantification of mitotic cells from D.. F. Western blot to detect cleavage of PARP protein, an indicator of apoptotic cell death, in NPC-CB660 and three GSC isolates after knockdown of ZNF131. Cells were assayed 48hrs post-selection after LV-shRNA infection (n = 3). G. RT-qPCR analysis of ZNF131 kd in NPCs and GSCs. Cells were assayed 48hrs post-selection after LV-shRNA infection (n = 3). H. Suppression of growth defects caused by shZNF131 using shRNA resistant ZNF131 ORF. Cells were first infected with LV containing control or shRNA resistant ORF followed by LV-shRNA and assayed for cell growth in monolayer culture 7 days post selection (n = 3). Target sites for ZNF131 shRNAs #1 and #2 where both mutated in the ORF construct and thus made resistant, while the site for shRNA #3 was left unchanged. I. Western blots of shRNA resistant ORF expression. *indicates p < .01 student's t-test.
