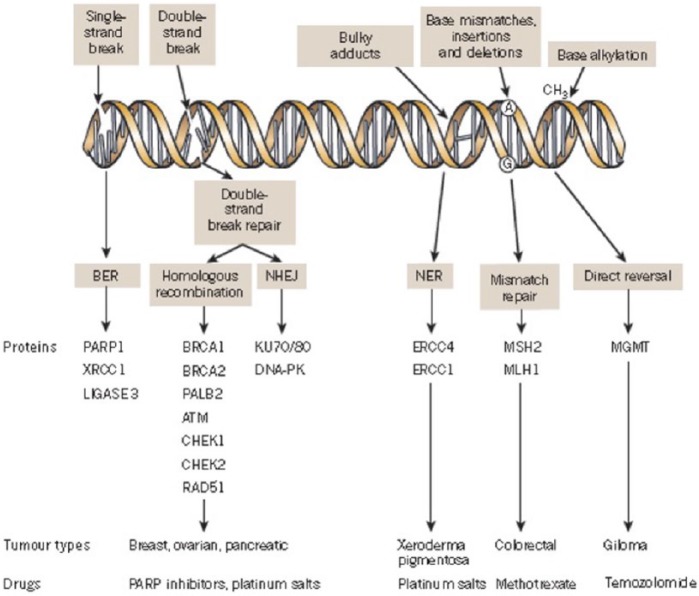
Figure 1.
A panoply of DNA repair mechanisms maintains genomic stability. DNA is continually exposed to a series of insults that cause a range of lesions, from single-strand breaks (SSBs) to base alkylation events. The choice of repair mechanism is largely defined by the type of lesion, but factors such as the stage of the cell cycle also have a role. Key proteins involved in each DDR mechanism, the tumour types usually characterized by DDR defects and the drugs that target these defects are shown. Figure modified, with permission, from Lord and colleagues 2012.
BER, base excision repair; DDR, DNA damage response; NER, nucleotide excision repair; NHEJ, non-homologous end joining.