Fig. 1.
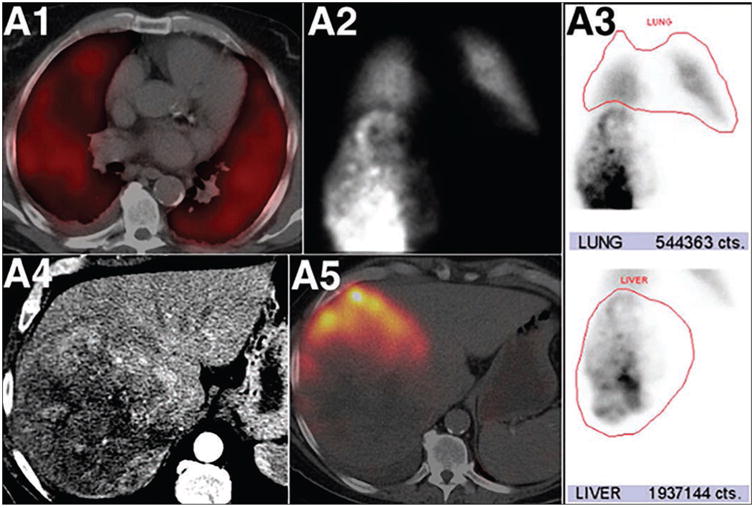
Marked pulmonary 99mTc-macroaggregated albumin (MAA) shunting in patient with hepatocellular carcinoma. Fused SPECT/CT axial image (A1) of chest shows diffuse 99mTc-MAA pulmonary activity in relation to shunted MAA particles. Anterior planar static image (A2) of chest and upper abdomen after 99mTc-MAA administration into right hepatic artery shows heterogeneous 99mTc-MAA distribution activity in liver and diffuse pulmonary activity. ROIs around lung and liver (red outlines, A3) lead to calculation of high lung shunt fraction of 21.9%. Axial contrast-enhanced CT (A4) shows large heterogeneous right liver mass. Fused SPECT/CT image of liver (A5) does not show significant localization of 99mTc-MAA in right liver mass. High lung shunt fraction precluded this patient from radioembolization therapy. This research was originally published in JNM. Uliel L, Royal HD, Darcy MD, et al. From the angio suite to the gamma-camera: vascular mapping and 99mTc-MAA hepatic perfusion imaging before liver radioembolization—a comprehensive pictorial review. J Nucl Med 2012; 53:1736–1747. © by the Society of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging, Inc.
