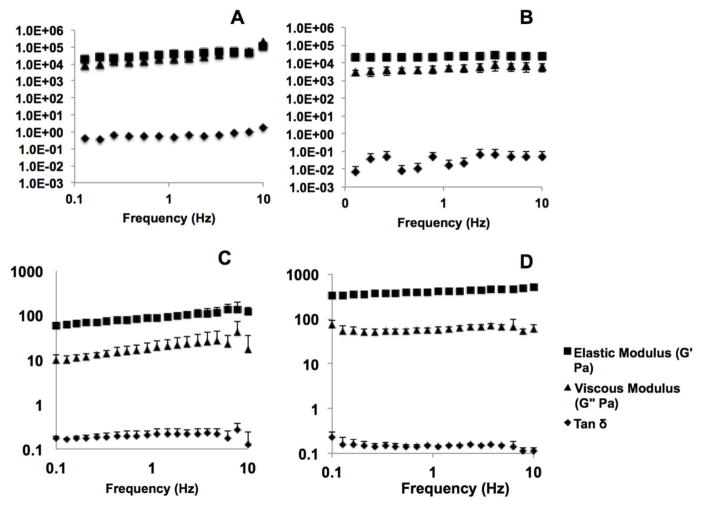
Figure 4.
Rheological characterization of (A) 20% KOS hydrogels, (B) 20% KTN hydrogels, (C) 12% KOS hydrogels and (D) 8% KTN hydrogels as determined by a frequency sweep for the elastic modulus (G′), viscous modulus (G″) and tan δ. Both types of keratin hydrogels show near independence with frequency and a tan δ value of less than 1, indicating the formation of stable hydrogels. The viscous modulus for KTN exhibits less dependence with frequency than KOS, and both G′ and G″ are approximately an order of magnitude higher in KTN than KOS (note the log-log nature of the plot), likely due to the presence of disulfide crosslinks with the material. Error bars denote standard deviation.