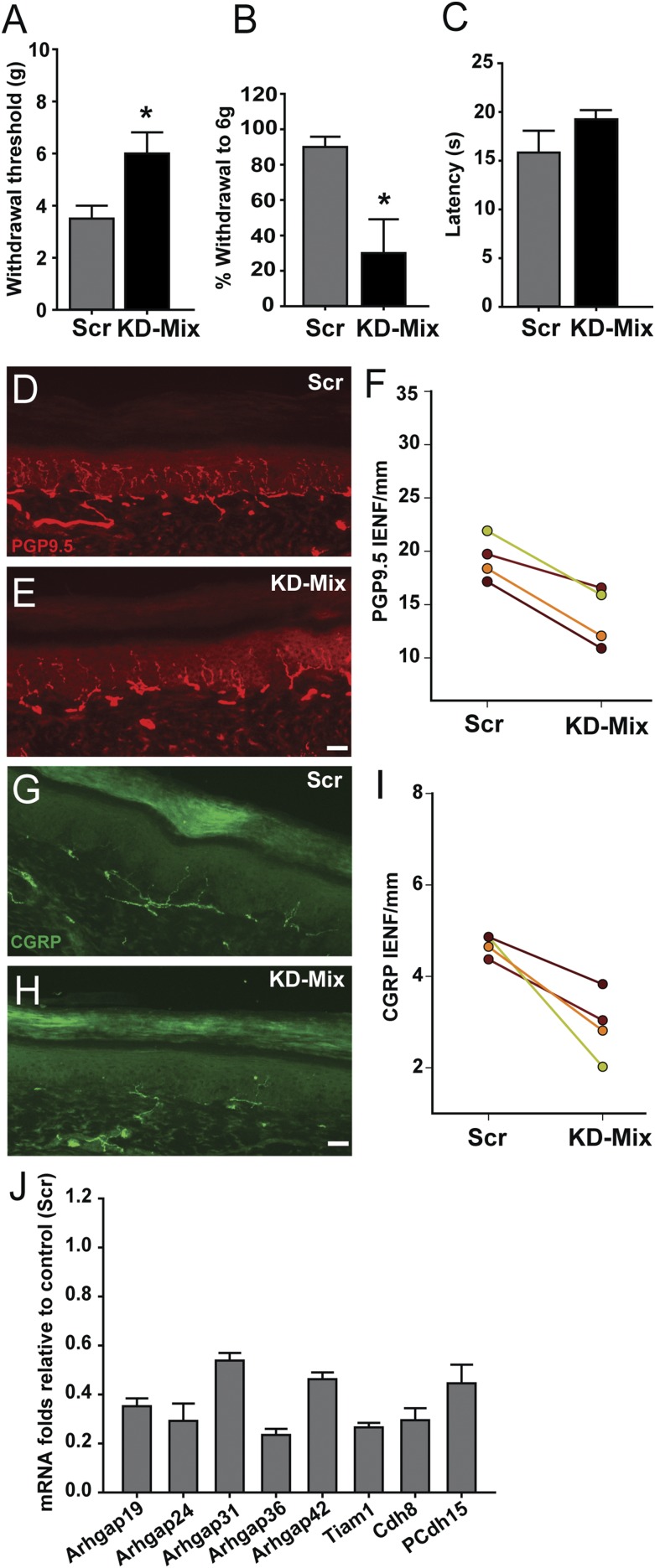
Fig. 7.
Down-regulating key cytoskeleton-related genes normalizes neuroanatomical and behavioral phenotypes in Mecp2−/y rats. (A) Thirty days following lentiviral shRNA mixture injection (KD-Mix) into the hind paw, withdrawal threshold to mechanical stimulation was increased relative to scrambled shRNA control injection (*P = 0.04). (B) shRNA knockdown also reduced responsiveness to a subthreshold stimulus (*P = 0.024). (C) shRNA knockdown did not elicit a significant change in hind paw heat sensitivity (P = 0.11). (D) PGP9.5 labeling in scrambled-injected footpad shows innervation characteristic of Mecp2−/y KO rats. (E) PGP9.5-ir innervation appeared less after knockdown mixture injection. (F) Quantification confirmed reduced IENF per millimeter following knockdown mixture injection (P = 0.006). (G) Peptidergic innervation in Mecp2−/y footpad injected with scrambled shRNA revealed by CGRP immunostaining. (H) Peptidergic innervation appeared reduced following knockdown mixture-injected footpad. (I) Quantitation confirmed reduced peptidergic innervation after knockdown injection (P = 0.021). n = 4 Mecp2−/y rats in A, B, C, F, and I. (Scale bar, 50 µm.) (J) qPCR analysis of primary sensory neurons derived from footpad-injected rats and selected for GFP expression by FACS shows target gene down-regulation relative to scrambled transduced neurons (n = 4 samples each for scrambled and mixture).