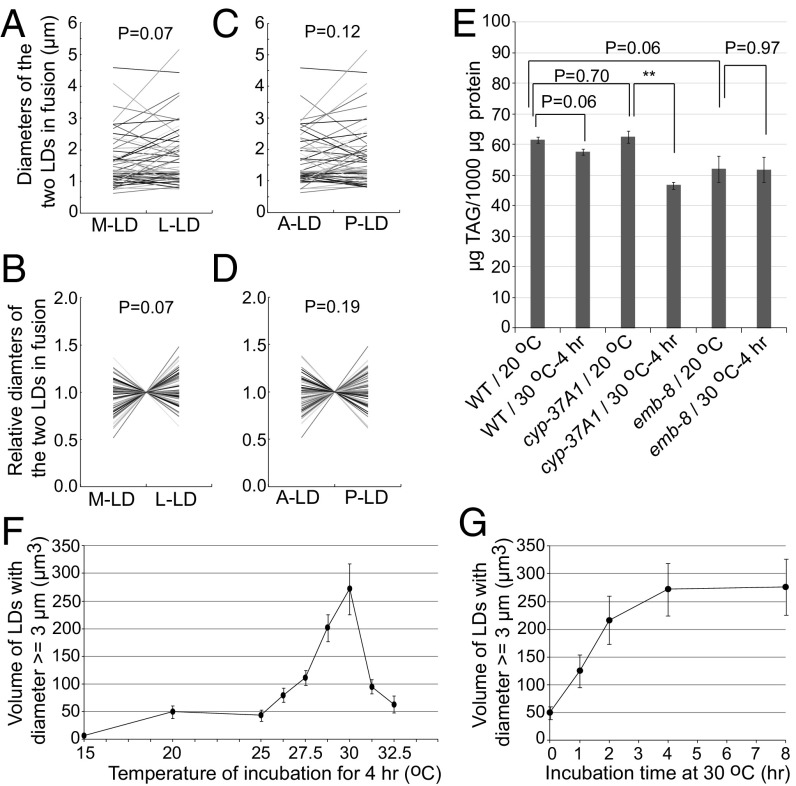
Fig. 2.
Mutation of cyp-37A1 derepresses a nonasymmetric and thermosensitive LD fusion process. (A–D) The two fusing LDs are designated as medial (M) vs. lateral (L), or anterior (A) vs. posterior (P). The absolute diameters of the two LDs (A and C) and relative diameters normalized to the mean (B and D) are plotted as connecting lines. No significant size asymmetry is found between the two LDs. Paired two-sample t test. n = 57. (E) There is no significant difference of TAG level between WT and cyp-37A1(ssd9)/emb-8(ssd89), between before and after fusion for WT and emb-8(ssd89). There is a small but significant decrease after fusion for cyp-37A1(ssd9). Data are mean ± SEM. n = 3 for WT and cyp-37A1(ssd9); n = 7 for emb-8(ssd89). **P ≤ 0.01. Unpaired two-sample t test. (F and G) The volume of supersized LDs formed in the second intestine in cyp-37A1(ssd2); glo-4(ok623) is used to quantitate the fusion rate upon different temperature treatment or with different treatment time. Fusion starts at 25 °C, peaks at 30 °C, and declines beyond 30 °C (F). Fusion in cyp-37A1(ssd2); glo-4(ok623) increases over time and plateaus at 4 h, displaying a first-order kinetics (G). Data are mean ± SEM. n ≥ 10.