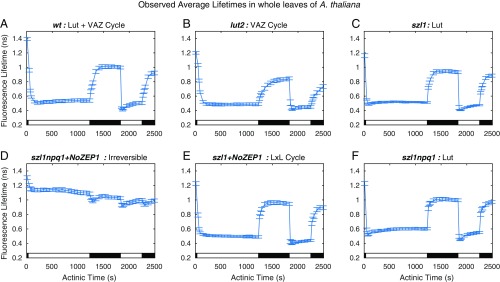
Fig. 2.
Average fluorescence lifetime traces over a two-cycle light acclimation scheme shown by the light and dark bars superimposed on the bottom of each plot for six A. thaliana strains. Error bars denote SD for n = 20. (A) The wt contains lutein and a VAZ cycle to form zeaxanthin in high light conditions. (B) The lut2 lacks lutein and has an active VAZ cycle. (C) The szl1 lacks zeaxanthin because of a partially blocked β-carotene biosynthesis pathway and contains more lutein than wt. (D) The szl1npq1+NoZEP1 strain does not have either xanthophyll cycle. (E) The szl1+NoZEP1 lacks zeaxanthin and contains a nonnative zeaxanthin epoxidase that functions on lutein, converting lutein to lutein epoxide that can be converted back to lutein by native VDE in high light. (F) The szl1npq1 contains lutein but lacks zeaxanthin because of blocking of the β-carotene biosynthesis pathway and inhibition of VDE.