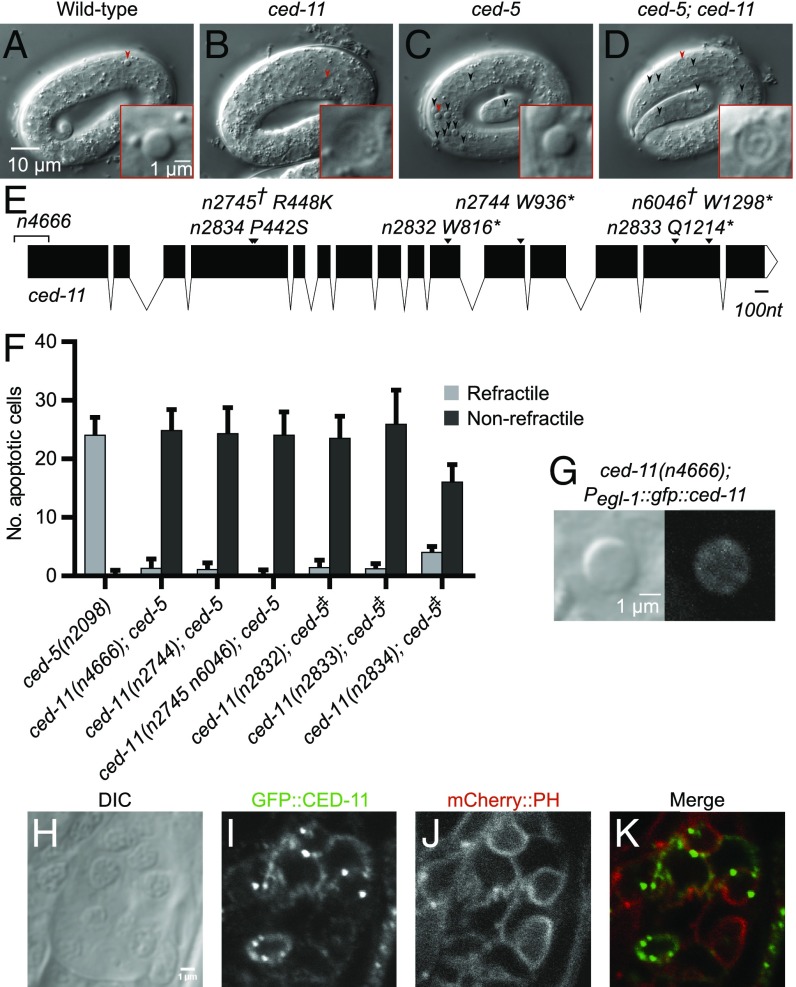
Fig. 1.
ced-11 is required for the increase in apoptotic cell refractility. (A–D) DIC images of threefold-stage embryos. Arrowheads indicate apoptotic cells that are shown in the Insets. (A) Wild-type embryo with refractile apoptotic cell. (B) ced-11(n2744) embryo with nonrefractile apoptotic cell. (C) ced-5(n2098) embryo with accumulated refractile apoptotic cells. (D) ced-11(n2744); ced-5(n2098) embryo with accumulated nonrefractile apoptotic cells. (E) Diagram of the ced-11 gene. Arrows indicate the location of the ced-11 allele. The asterisk indicates the stop codon. The dagger indicates two ced-11 mutations isolated in the same strain. The bracket indicates a deletion. (F) Average numbers of refractile and nonrefractile apoptotic cells in the heads of threefold-stage embryos of the indicated genotypes. ced-5(n2098) was in all strains. The double-dagger indicates that the strain also includes sem-4(n1378). Error bars indicate SD. (n > 20). (G) DIC and GFP images of a refractile apoptotic cell that expresses GFP::CED-11 in a ced-11(n4666) embryo [ced-11(n4666); nEx2544[Pegl-1::gfp::ced-11]. (H–K) Head of an L1 larva showing expression of nIs790[Pced-11::gfp::ced-11]; nEx2344[Pevl-20::mCherry::ph. (H) DIC. (I) GFP::CED-11 expression in multiple cells. (J) Plasma membrane marker mCherry::PH. (K) Merged image shows colocalization of GFP::CED-11 and mCherry::PH.