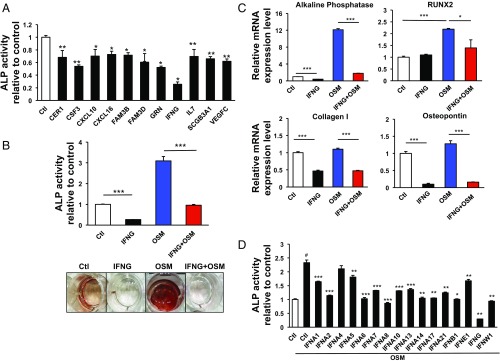
Fig. 2.
Identification of IFNG as a potent negative regulator for cytokine-induced differentiation of DPSCs. (A) Out of 11 identified negative regulators, IFNG most strongly inhibited odontoblastic differentiation based on ALP assay results. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01. Data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 6). (B) ALP assays and ARS staining were performed to evaluate the effect of IFNG on DPSC differentiation under stimulation with OSM 10 d after lentivirus infection. IFNG prevented OSM-induced increases in ALP activity and ARS staining. ***P < 0.001. (C) qPCR analysis was used to determine mRNA levels of ALP, RUNX2, Collagen I, and Osteopontin, typical markers for DPSC differentiation. IFNG prevented OSM-induced up-regulation of all four markers. *P < 0.05, ***P < 0.001. (D) Several subtypes of IFN lentiviruses were tested for the effect on ALP activity in DPSCs under OSM stimulation 10 d after infection. *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ***P < 0.001 (comparison between OSM only vs. individual cytokines); #P < 0.001 [control (Ctl) vs. OSM only]. Data are shown as mean + SD (n = 3) in B to D.