Fig. 2.
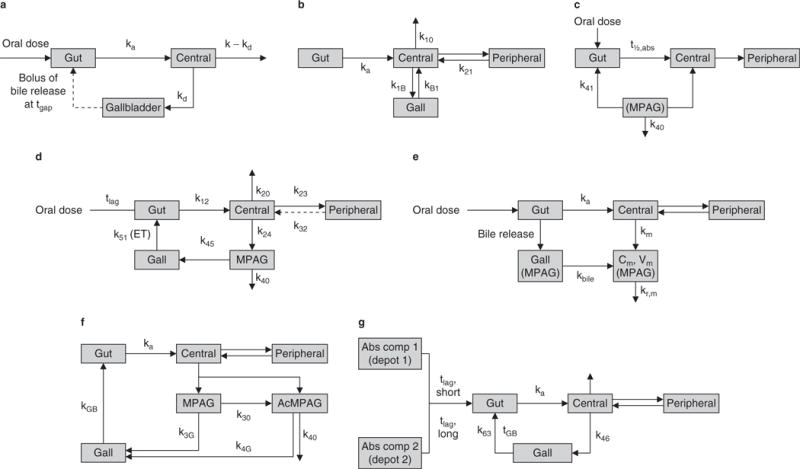
Schematicsof mycophenolic acid (MPA) pharmacokinetic models describing enterohepatic circulation (EHC). (a) 3-compartment EHC model based on a 1-compartment disposition model (reproduced from Funaki,[67] with permission). (b) Proposed EHC, 2-compartment structural model with first-order absorption with a lag time (tlag) [reproduced from Payen et al.,[68] with permission]. (c) 4-compartment model, with rate constant describing transfer from fourth to first compartment [enterohepatic recycling] (reproduced from Cremers et al.,[42] with permission). (d) Chain compartment model (intestinal, gallbladder, central and peripheral compartments for MPA and central compartment for 7-O-MPA-β-glucuronide (MPAG) [reproduced from Jiao et al.,[26] with permission]. (e) 5-compartment drug and metabolite EHC model with MPA and MPAG plasma concentrations simultaneously (reproduced from Yau et al.,[69] with permission). (f) 2-compartment model with linear elimination, with MPAG and MPA acyl-glucuronide (AcMPAG) produced from the central compartment with EHC of MPA via the two metabolites (reproduced from Sam et al.,[70] with permission). (g) 2-compartment model accounts for the enterohepatic recirculation of MPA. The absorption of MPA was described with two first-order processes with a short and a long tlag and subsequent first-order elimination (reproduced from de Winter et al.,[71] with permission). Abs comp=absorption compartment; Cm = concentration of MPAG in central compartment; ET = gallbladder emptying time; Gall = amount of MPAG in gallbladder compartment; Gut= amount of MPA in gut compartment; k=first-order rate constant; kxy = transfer rate constant from compartment x to y; ka= absorption rate constant; kbile= biliary excretion rate; kd= excretion rate constant into gallbladder; kGB = rate constant for the release of recirculated MPA from MPAG and AcMPAG; km = formation rate; kr,m = renal excretion rate of MPAG; t½,abs = absorption half-life; tgap = expulsion time of gallbladder; tGB = time of gallbladder compartment opening; Vm= volume of MPAG in central compartment.
