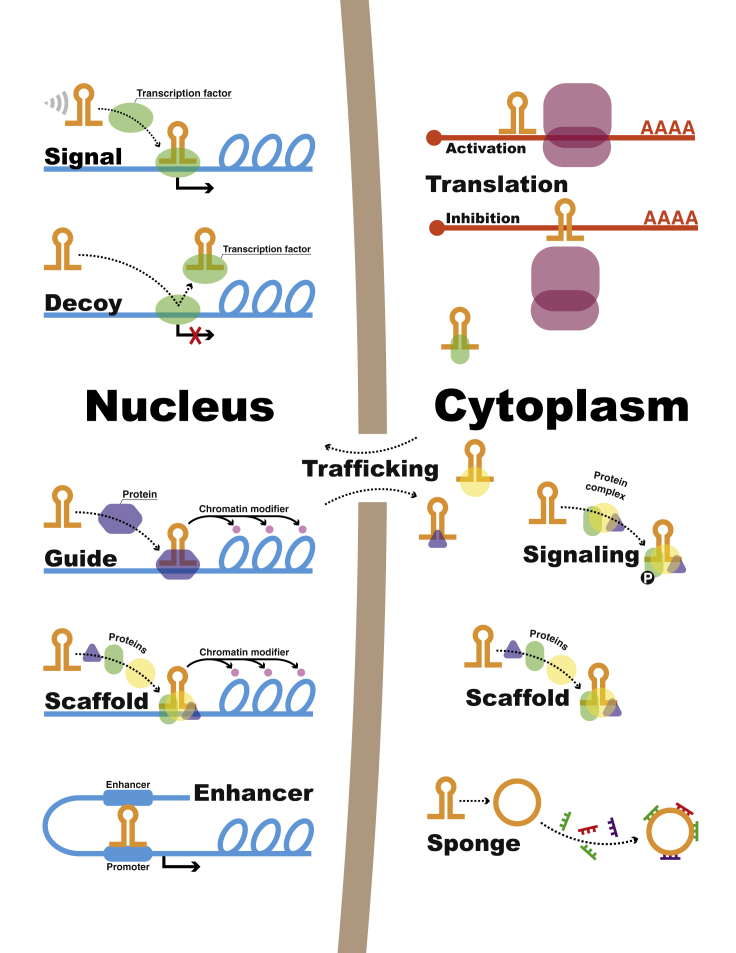
Figure 1.
Classification of lncRNAs by Mechanism of Action
Signal lncRNAs respond to specific stimuli and thus show expression specific to cell type. Decoys bind transcription factors and other proteins away from their target site, repressing transcription. Guides interact with regulatory proteins, forming ribonucleoprotein complexes, and direct them to their target sites in subcellular locations. Scaffolds serve as platforms to bring different proteins together, both in the cytoplasm and in the nucleus, activating or repressing transcription. Enhancers are regulatory sequences in which transcription factors bind to initiate transcription; these regions of the genome produce several transcripts, enhancer lncRNAs, which act in cis to regulate expression of target genes. In the cytoplasm, lncRNAs can activate or inhibit translation by binding to target mRNAs. They can also regulate protein trafficking and signaling, such as phosphorylation. Sponging miRNAs is another way lncRNAs (including circular RNAs) regulate gene expression post-transcriptionally.