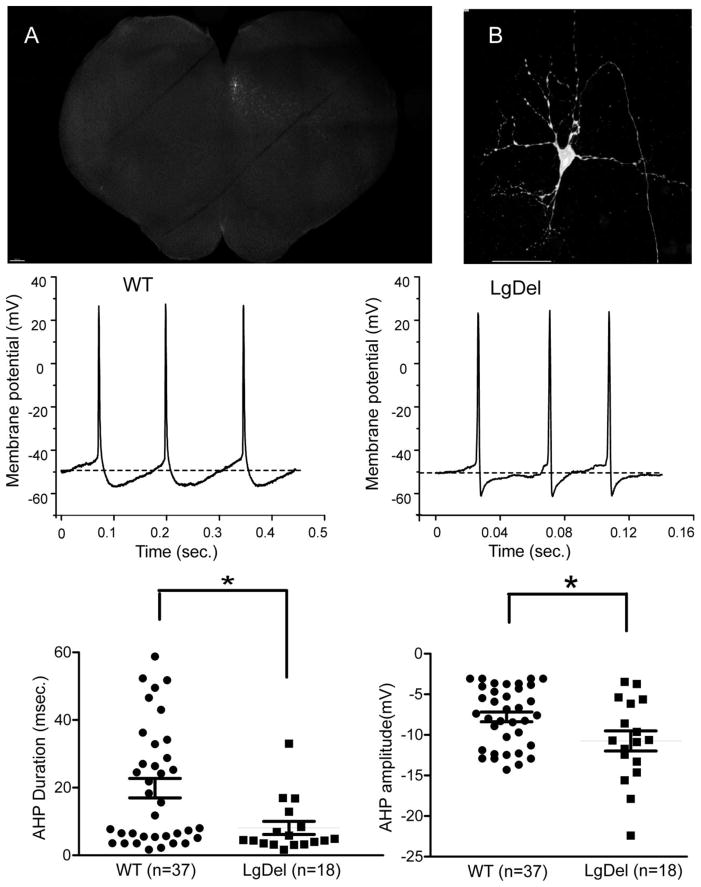
Figure 1. The after-hyperpolarization potential (AHP) following action potential firing of hypoglossal neurons was significantly altered in LgDel P7-P14 mouse pups.
A brainstem slice with a single patched, biocytin filled neuron (arrow) within the hypoglossal nucleus is displayed in figure 1A and 1B. Figure 1B shows the biocytin-labeled patched hypoglossal neuron, with a large soma, multiple dorso-ventral oriented dendrites, and a genual axon characteristic of these cranial motor neurons. The middle two traces show typical examples of hypoglossal motor neurons (XII MNs) spontaneous firing spikes in wild type (left) and LgDel mice (right), the dashed line defining the resting Vm. In current clamp configuration XII MNs in LgDel mice possess a larger AHP amplitude but a shorter duration of AHP than wild type mice. Bottom scatter plots present statistic data. *p≤0.05. **p≤0.01, ***p≤0.001 for this and all following graphs. Scale bar: 200μm (fig. 1A), 20μm (fig. 1B).