Figure 5.
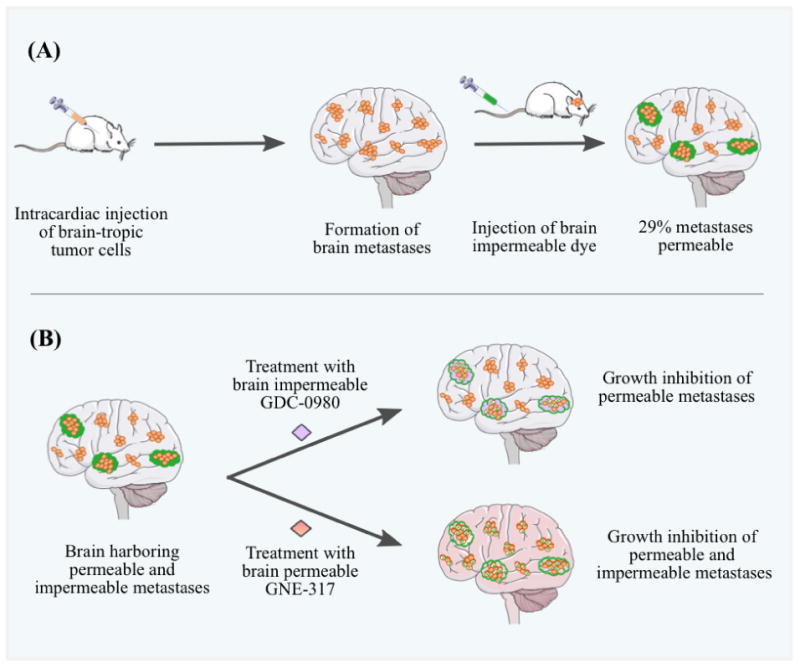
The role of BBB permeability in the efficacy of targeted therapies for the treatment of brain metastases. A, injection of brain-tropic A2058 melanoma cells (orange) into the left cardiac ventricle of mice led to the formation of MBMs. Sodium fluorescein (green), a brain-impermeable dye, was injected intravenously via tail vein, and its uptake into metastatic lesions was measured and used as a marker of brain metastasis permeability. Only ∼29% of the brain metastases were permeable to the administered dye (green clouds). B, mice harboring both permeable (green clouds) and impermeable (no clouds) brain metastases were randomized to vehicle or two PI3K inhibitors, GDC-0980, which is brain-impermeable, or GNE-317, which has demonstrated brain permeability. Both GDC-0980 and GNE-317 inhibited the growth of permeable metastases, while only the brain-permeable GNE-317 inhibited the growth and caused tumor apoptosis (white tumor cells with X) of impermeable metastases. These observations confirm a functional contribution of brain permeability to drug efficacy for brain metastases treatment (modified and redrawn from (Steeg et al. 2016)). (2-column fitting image)
