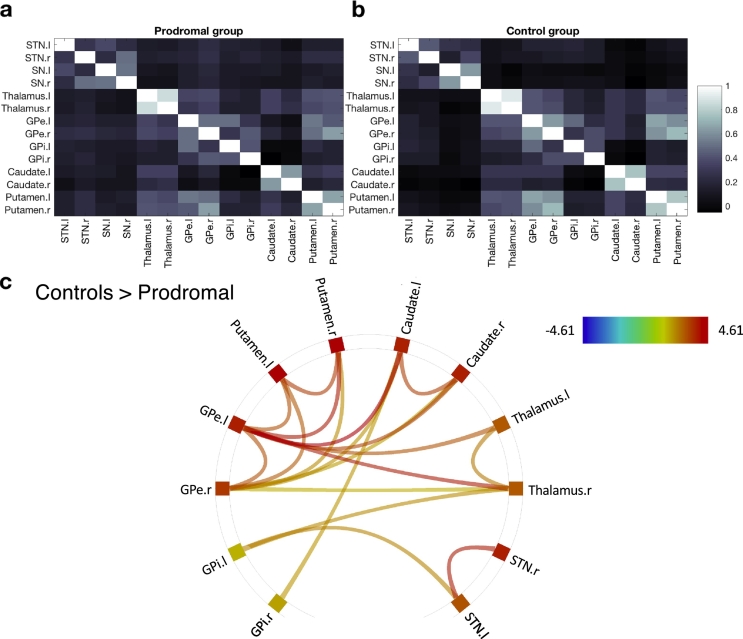
Fig. 1.
Region-to-region functional interactions in the basal ganglia. (a) Average functional connectivity within the basal ganglia network in the prodromal group (b). Average BG functional connectivity in the control group. All correlation values were inverse Fisher Z transformed (to Pearson's r values) for visualization purposes. (c) Functional connections for which the prodromal group showed reduced connectivity relative to the control group, based on a non-parametric network-based statistics analysis (family-wise error correction, p-FWE < 0.05) coupled with a seed-level threshold set at p-FDR < 0.05. Shown are pairs of network nodes between which the resting-state times series correlations were weaker in the prodromal group than in the control group. Colored lines depict the strength of the test statistic.