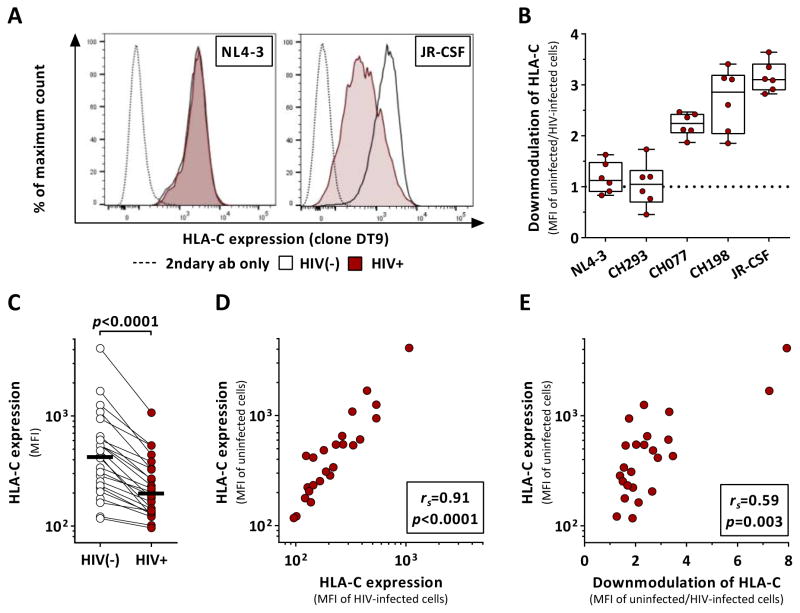
Figure 1. HIV-1 clones differentially modulate HLA-C expression after in vitro infection.
Effects of HIV-1 infection on HLA-C surface expression on primary CD4+ T cells as determined by flow cytometry. (A) HLA-C levels of infected and uninfected cells after infection with NL4-3 and JR-CSF. (B) Extent of HIV-1-mediated HLA-C downmodulation across various HIV-1 clones as determined by the ratio between HLA-C expression (median fluorescence intensity, MFI) of uninfected and infected cells (n=6). Box plots define median and IQR. (C) Baseline HLA-C expression of uninfected CD4+ T cells (clear) and after infection with JR-CSF (red) (n=24). Black bars represent the median. (D) Correlation analysis of HLA-C levels (MFI) between uninfected and JR-CSF-infected CD4+ T cells. (E) Correlation analysis between baseline HLA-C expression levels of uninfected CD4+ T cells and the extent of HIV-1-mediated HLA-C downmodulation. Statistical analyses: Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test and Spearman rank correlation. See also Figure S3.