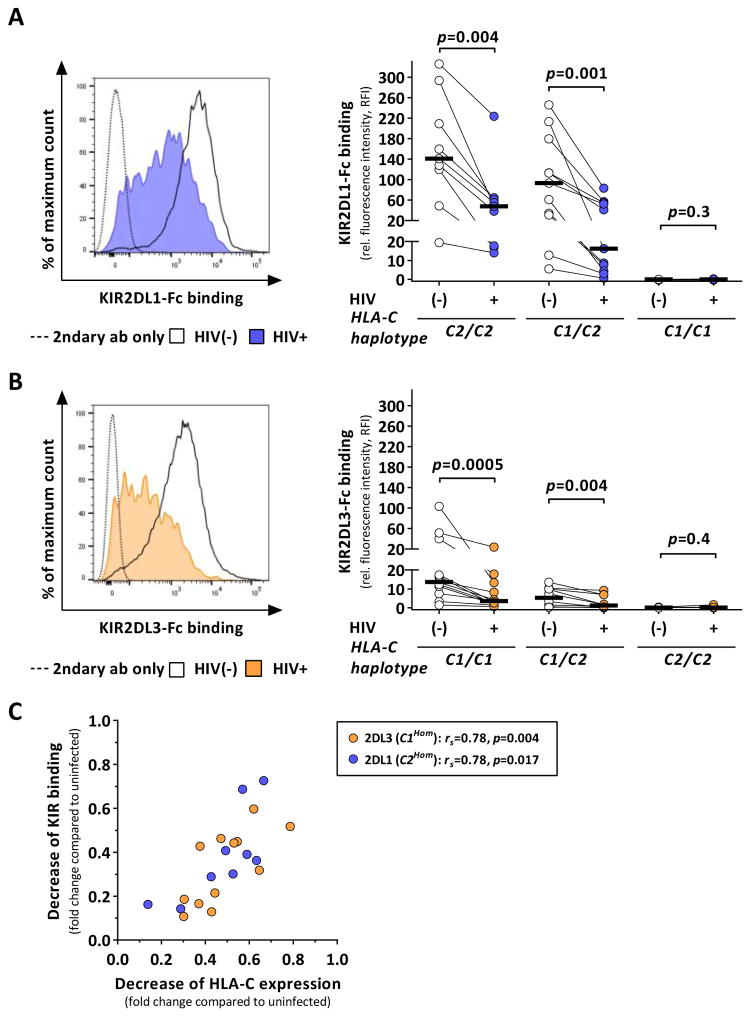
Figure 2. HIV-1 infection alters binding of KIR2DL1 and KIR2DL3 to HLA-C.
KIR binding to HIV-1-infected and uninfected CD4+ T cells measured by flow cytometry and stratified by donor HLA-C haplotypes (C2Hom: n=9; C1/2: n=11; C1Hom: n=12). (A and B) KIR binding to infected cells after infection with JR-CSF (KIR2DL1: blue; KIR2DL3: yellow) as compared to uninfected cells (clear) displayed as relative fluorescence intensity. Black bars represent the median. (C) Correlation analysis between HIV-1-associated reduction of HLA-C expression and KIR binding on infected cells given as fold change reduction compared to uninfected cells. KIR2DL1 binding to cells from C2Hom donors (n=9) are displayed in blue, KIR2DL3 binding to cells from C1Hom donors (n=12) in yellow. Statistical analyses: Wilcoxon matched-pairs signed rank test and Spearman rank correlation. See also Figure S1 and S3.