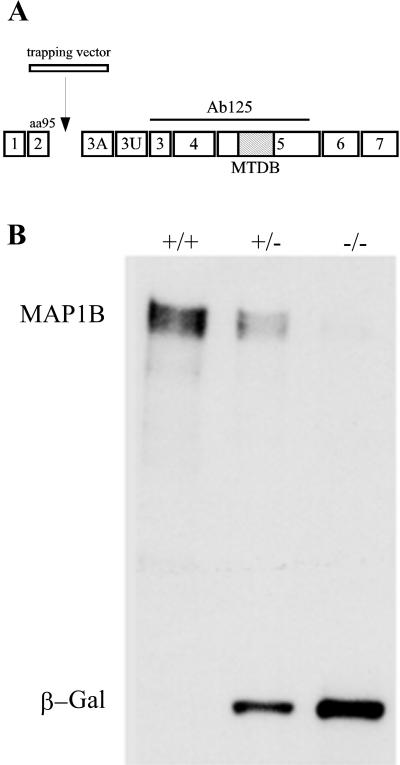
Figure 1.
(A) Structure of MAP1B gene. Seven coding exons (1–7) and two noncoding ones (3A and 3U) of the MAP1B protein are shown. The trapping vector insertion occurs immediately after exon 2, which encodes the N-terminal 95 amino acids of the protein. The epitope of antibody 125 used to confirm the genotype of animals is depicted as a straight line. The hatched box represents the microtubule-binding domain (MTBD). (B) Western blot analysis of spinal cord extracts from wild-type (+/+), heterozygous (+/−), and homozygous (−/−) MAP1B mutant mice reacted with a mAb against MAP1B and β-galactosidase (β-Gal). Note that the extracts obtained from the homozygous (−/−) MAP1B contain trace amounts of MAP1B and high levels of β-Gal. Ten micrograms of protein was loaded in each lane.