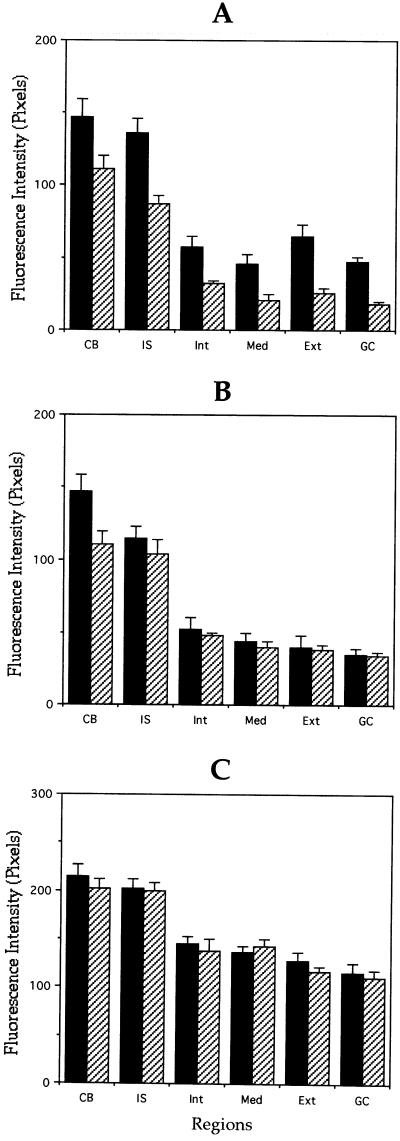
Figure 4.
Quantitation of microtubule polymer content of control and MAP1B-deficient neurons. (A and B) Quantitative measurements of β-tubulin fluorescence intensity in axons (A) and minor processes (B) from wild-type (▪) and MAP1B-deficient (▨) cultured neurons. For these experiments, cells were extracted with detergents before fixation under microtubule-stabilizing conditions (see MATERIALS AND METHODS). Fluorescence intensity measure ments were performed in the cell body (CB) and along neurites. Within neurites measurements were performed in the initial segment (IS), inner segment (Int), middle segment (Med), external segment (Ext), and growth cones (GC) of axons and minor processes. Note that β-tubulin fluorescence intensity is dramatically reduced in the external axonal segment and in axonal growth cones (C). Equivalent measurements to those shown in A, but from cells extracted with detergents after fixation. Note that there are no significant differences in fluorescence intensity between WT and MAP1B-deficient neurons. A total of 75 cells was analyzed for each experimental condition. Each value represents the mean ± SEM.