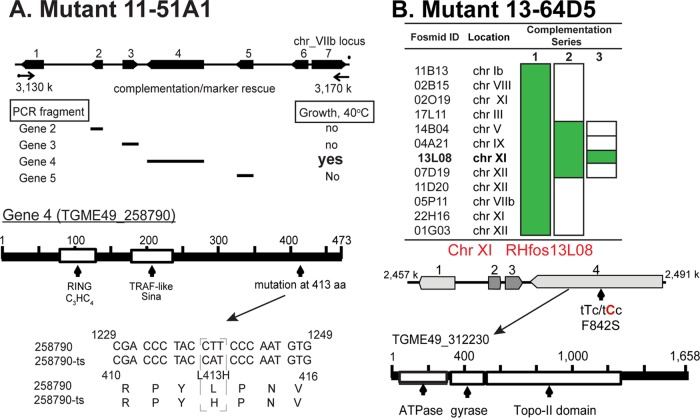
FIG 2 .
Identification of the defective genes in ts mutants 13-64D5 and 11-51A1. (A) Genetic complementation of ts mutant 11-51A1 with cosmid genomic libraries followed by marker rescue identified the defective locus to chromosome (chr) VIIb (see top diagram). The locus was further resolved using PCR products spanning each of the central four genes. Only gene 4 (TGME49_258790) rescued ts mutant 11-51A1 at 40°C and was sequenced to identify the ts mutation. The mutation and size and major protein domains for gene 4 are shown. aa, amino acid. (B) The genome of ts mutant 13-64D5 was sequenced to >150-fold coverage identifying 16 nonsynonymous mutations. Fosmid clones from a mapped T. gondii genetic library that spanned 12 of the sequenced mutations were combined and used to successfully complement ts mutant 13-64D5 (complementation series 1). Genetic complementation with fosmid clones remixed into three groups (series 2) followed by complementation of four individual fosmids (series 3) identified a region on chromosome XI as the locus carrying the mutation responsible for high temperature sensitivity. In the identified XI locus, ts mutant 13-64D5 harbors a single mutation (F842S) in a T. gondii ortholog of topoisomerase II (TgTopo-II) that is rescued by parental copy of TgTopo-II on fosmid RHfos13L08. Fosmid ID, fosmid identification.