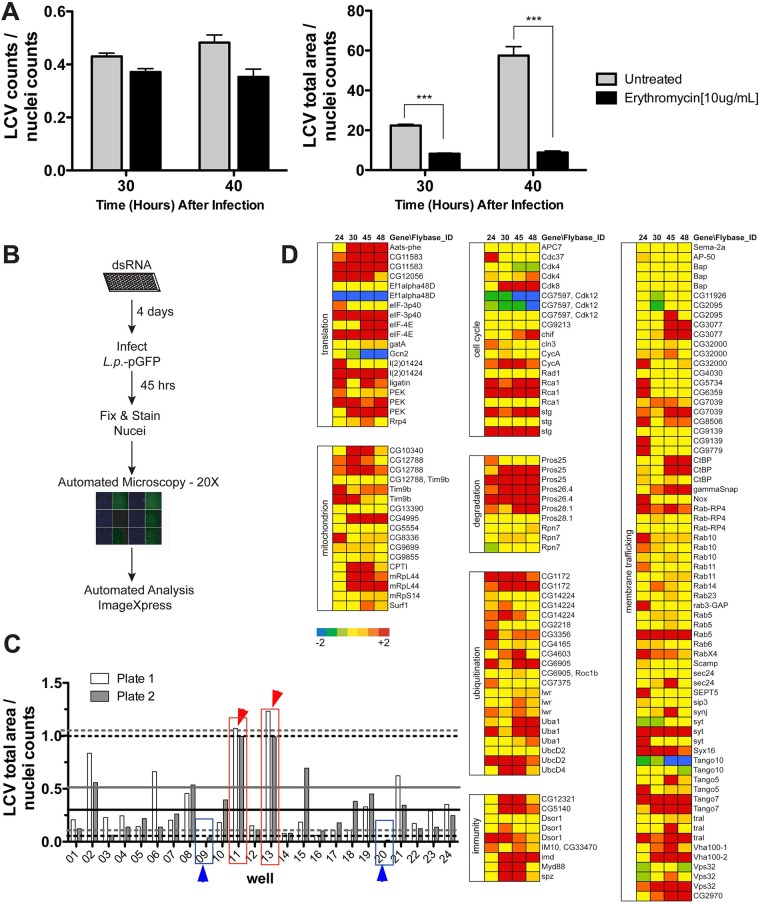
FIG 1 .
dsRNA screen in D. melanogaster cells to identify host factors involved in restriction of L. pneumophila intracellular growth. (A) The screening strategy allows detection of bacteria with altered intracellular replication. Drosophila cells were challenged with the Lp01 strain at the noted time points in absence or presence of erythromycin, added at 19 h postinfection. The total number of Legionella vacuoles was counted by automated microscopy (right panel), and the total LCV area (left panel) was calculated at 30 and 40 hpi and normalized to cell nuclei (Materials and Methods). (B) Flow chart representation of the dsRNA interference screen strategy used in D. melanogaster cells to identify host factors that modulate L. pneumophila intracellular growth. (C) Strategy for identification of hits with altered levels of bacterial growth during the screen. Phenotypes of interest due to increased levels of L. pneumophila growth are shown in red; phenotypes of interest due to reduced bacterial growth are shown in blue. Upper dashed lines represent the value for Z = 2 above the mean for each plate. Lower dash lines represent the value for Z = 1.5 below the mean for each plate. Solid lines represent the mean for each plate. Black lines, plate 1; gray lines, plate 2. (D) Candidate dsRNAs that result in enhanced L. pneumophila growth. In the secondary screen, Lp01 lux+ was introduced onto Drosophila cell monolayers, and luminescence was measured at the indicated times (hours) after uptake as a readout for growth. The color scale (displayed below the left column) represents SD from the mean replication levels obtained in an untreated control plate. Genes were categorized based on their function or host cell process.