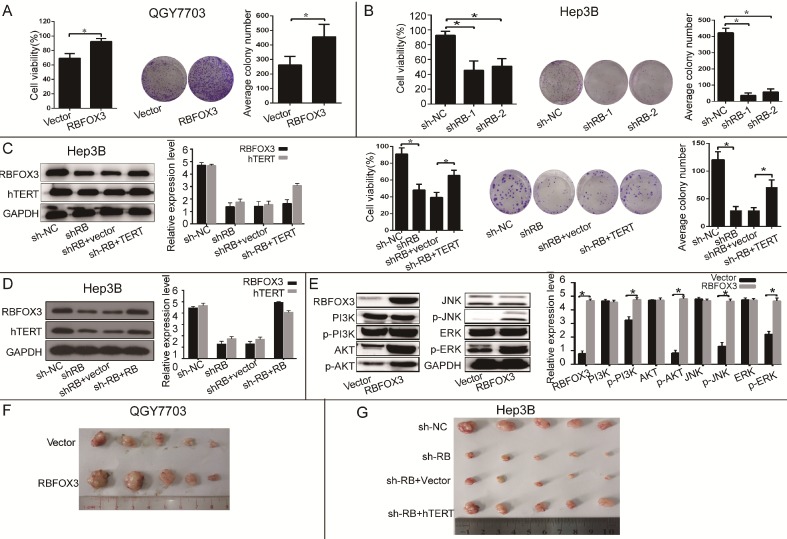
Figure 3.
RBFOX3 regulated HCC cell growth via hTERT signaling pathway. (A) RBFOX3 overexpression increased propagative cell viability (left panel) and colony formation capacity (middle panel) in QGY7703 cells. Right panel showed the quantification of colonies. (B) RBFOX3 depletion decreased cell viability (left panel) and colony formation capacity (middle panel) in Hep3B cells. Right panel showed the quantification of colonies. (C) Overexpression of hTERT reversed the inhibition of hTERT expression, cell viability and colony formation mediated by RBFOX3 knockdown in Hep3B cells. Cell viability was determined by absorbance at the wavelength of 490 nm and normalized to the absorbance value in the control group by MTS assay. The absorbance value was shown as means ± SD. (D) Overexpression of RBFOX3 reversed the inhibition of hTERT expression by RBFOX3 knockdown in Hep3B cells. (E) RBFOX3 regulated the expression of the PI3K/AKT signaling proteins. Overexpression of RBFOX3 activated hTERT downstream PI3K/AKT signaling pathway in QGY7703 cells. The protein level of p-PI3K, p-AKT, p-JNK, p-ERK and total PI3K, AKT, JNK and ERK were detected and quantified in RBFOX3 overexpressing QGY7703 cells, GAPDH was used as a loading control. (F) QGY7703 cells with RBFOX3 overexpressing plasmid or vector control were subcutaneously implanted into nude mice. The tumor grafts were excised 21 days after inoculation. (G) Hep3B cells with sh-RBFOX3, sh-NC, sh-RBFOX3+hTERT or sh-RBFOX3+vector were subcutaneously implanted into nude mice. The tumor grafts were harvested 21 days after inoculation.