Abstract
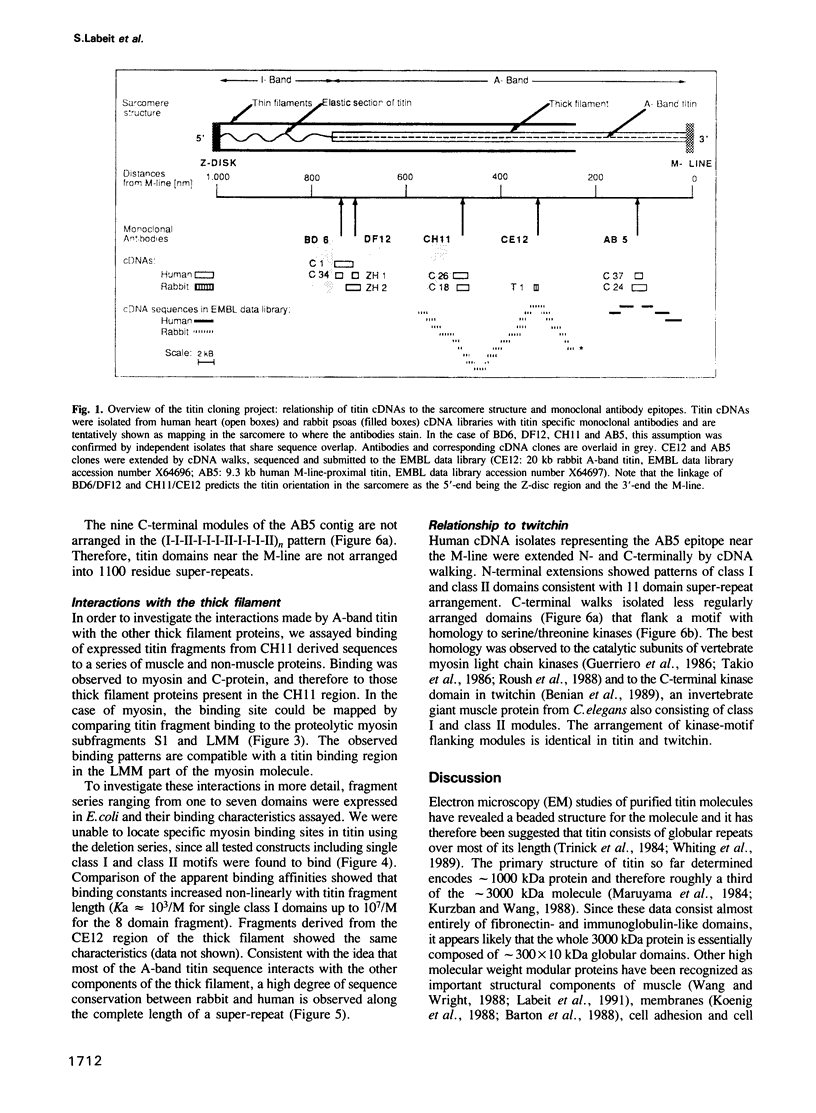
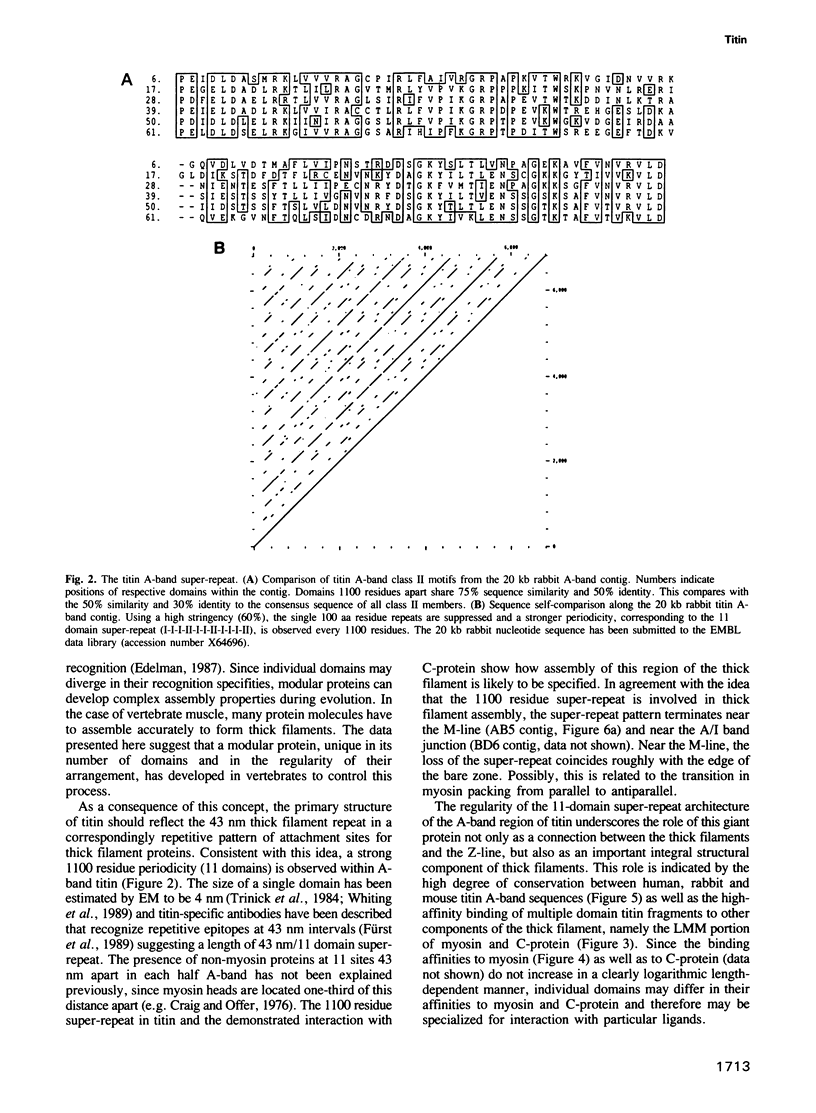
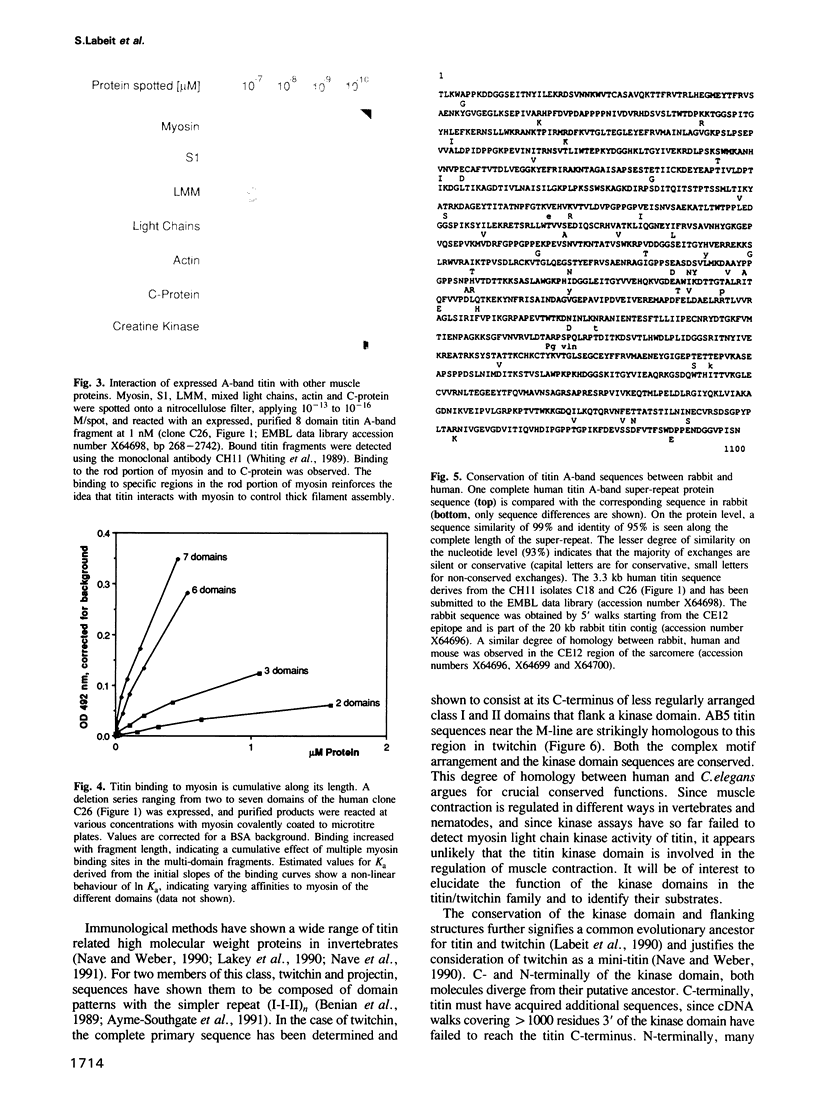
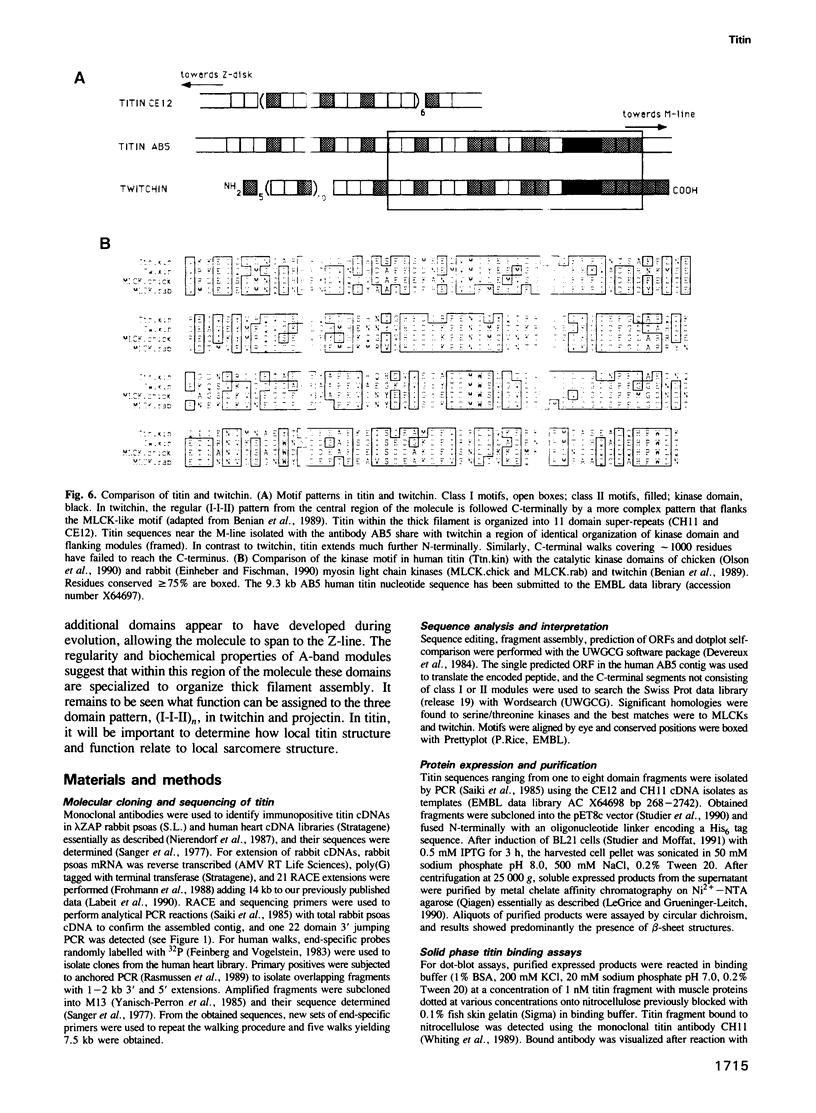
Titin is at present the largest known protein (M(r) 3000 kDa) and its expression is restricted to vertebrate striated muscle. Single molecules span from M- to Z-lines and therefore over 1 micron. We have isolated cDNAs encoding five distant titin A-band epitopes, extended their sequences and determined 30 kb (1000 kDa) of the primary structure of titin. Sequences near the M-line encode a kinase domain and are closely related to the C-terminus of twitchin from Caenorhabditis elegans. This suggests that the function of this region in the titin/twitchin family is conserved throughout the animal kingdom. All other A-band sequences consist of 100 amino acid (aa) repeats predicting immunoglobulin-C2 and fibronectin type III globular domains. These domains are arranged into highly ordered 11 domain super-repeat patterns likely to match the myosin helix repeat in the thick filament. Expressed titin fragments bind to the LMM part of myosin and C-protein. Binding strength increases with the number of domains involved, indicating a cumulative effect of multiple binding sites for myosin along the titin molecule. We conclude that A-band titin is likely to be involved in the ordered assembly of the vertebrate thick filament.
Full text
PDF

Images in this article
Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- Ayme-Southgate A., Vigoreaux J., Benian G., Pardue M. L. Drosophila has a twitchin/titin-related gene that appears to encode projectin. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1991 Sep 15;88(18):7973–7977. doi: 10.1073/pnas.88.18.7973. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Barton C. H., Dickson G., Gower H. J., Rowett L. H., Putt W., Elsom V., Moore S. E., Goridis C., Walsh F. S. Complete sequence and in vitro expression of a tissue-specific phosphatidylinositol-linked N-CAM isoform from skeletal muscle. Development. 1988 Sep;104(1):165–173. doi: 10.1242/dev.104.1.165. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Benian G. M., Kiff J. E., Neckelmann N., Moerman D. G., Waterston R. H. Sequence of an unusually large protein implicated in regulation of myosin activity in C. elegans. Nature. 1989 Nov 2;342(6245):45–50. doi: 10.1038/342045a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Bugari G., Poiesi C., Beretta A., Ghielmi S., Albertini A. Quantitative immunoenzymatic assay of human lutropin, with use of a bi-specific monoclonal antibody. Clin Chem. 1990 Jan;36(1):47–52. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Colley N. J., Tokuyasu K. T., Singer S. J. The early expression of myofibrillar proteins in round postmitotic myoblasts of embryonic skeletal muscle. J Cell Sci. 1990 Jan;95(Pt 1):11–22. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.1.11. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Craig R., Offer G. The location of C-protein in rabbit skeletal muscle. Proc R Soc Lond B Biol Sci. 1976 Mar 16;192(1109):451–461. doi: 10.1098/rspb.1976.0023. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Devereux J., Haeberli P., Smithies O. A comprehensive set of sequence analysis programs for the VAX. Nucleic Acids Res. 1984 Jan 11;12(1 Pt 1):387–395. doi: 10.1093/nar/12.1part1.387. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Edelman G. M. CAMs and Igs: cell adhesion and the evolutionary origins of immunity. Immunol Rev. 1987 Dec;100:11–45. doi: 10.1111/j.1600-065x.1987.tb00526.x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Einheber S., Fischman D. A. Isolation and characterization of a cDNA clone encoding avian skeletal muscle C-protein: an intracellular member of the immunoglobulin superfamily. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2157–2161. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2157. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Feinberg A. P., Vogelstein B. A technique for radiolabeling DNA restriction endonuclease fragments to high specific activity. Anal Biochem. 1983 Jul 1;132(1):6–13. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(83)90418-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Frohman M. A., Dush M. K., Martin G. R. Rapid production of full-length cDNAs from rare transcripts: amplification using a single gene-specific oligonucleotide primer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1988 Dec;85(23):8998–9002. doi: 10.1073/pnas.85.23.8998. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Nave R., Osborn M., Weber K. Repetitive titin epitopes with a 42 nm spacing coincide in relative position with known A band striations also identified by major myosin-associated proteins. An immunoelectron-microscopical study on myofibrils. J Cell Sci. 1989 Sep;94(Pt 1):119–125. doi: 10.1242/jcs.94.1.119. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Osborn M., Nave R., Weber K. The organization of titin filaments in the half-sarcomere revealed by monoclonal antibodies in immunoelectron microscopy: a map of ten nonrepetitive epitopes starting at the Z line extends close to the M line. J Cell Biol. 1988 May;106(5):1563–1572. doi: 10.1083/jcb.106.5.1563. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Fürst D. O., Osborn M., Weber K. Myogenesis in the mouse embryo: differential onset of expression of myogenic proteins and the involvement of titin in myofibril assembly. J Cell Biol. 1989 Aug;109(2):517–527. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.2.517. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Guerriero V., Jr, Russo M. A., Olson N. J., Putkey J. A., Means A. R. Domain organization of chicken gizzard myosin light chain kinase deduced from a cloned cDNA. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 30;25(26):8372–8381. doi: 10.1021/bi00374a007. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isaacs W. B., Kim I. S., Struve A., Fulton A. B. Biosynthesis of titin in cultured skeletal muscle cells. J Cell Biol. 1989 Nov;109(5):2189–2195. doi: 10.1083/jcb.109.5.2189. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Koenig M., Monaco A. P., Kunkel L. M. The complete sequence of dystrophin predicts a rod-shaped cytoskeletal protein. Cell. 1988 Apr 22;53(2):219–228. doi: 10.1016/0092-8674(88)90383-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kurzban G. P., Wang K. Giant polypeptides of skeletal muscle titin: sedimentation equilibrium in guanidine hydrochloride. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1988 Feb 15;150(3):1155–1161. doi: 10.1016/0006-291x(88)90750-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Barlow D. P., Gautel M., Gibson T., Holt J., Hsieh C. L., Francke U., Leonard K., Wardale J., Whiting A. A regular pattern of two types of 100-residue motif in the sequence of titin. Nature. 1990 May 17;345(6272):273–276. doi: 10.1038/345273a0. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Labeit S., Gibson T., Lakey A., Leonard K., Zeviani M., Knight P., Wardale J., Trinick J. Evidence that nebulin is a protein-ruler in muscle thin filaments. FEBS Lett. 1991 May 6;282(2):313–316. doi: 10.1016/0014-5793(91)80503-u. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Lakey A., Ferguson C., Labeit S., Reedy M., Larkins A., Butcher G., Leonard K., Bullard B. Identification and localization of high molecular weight proteins in insect flight and leg muscle. EMBO J. 1990 Nov;9(11):3459–3467. doi: 10.1002/j.1460-2075.1990.tb07554.x. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Maruyama K., Kimura S., Yoshidomi H., Sawada H., Kikuchi M. Molecular size and shape of beta-connectin, an elastic protein of striated muscle. J Biochem. 1984 May;95(5):1423–1433. doi: 10.1093/oxfordjournals.jbchem.a134750. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Mierendorf R. C., Percy C., Young R. A. Gene isolation by screening lambda gt11 libraries with antibodies. Methods Enzymol. 1987;152:458–469. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(87)52054-7. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave R., Fürst D., Vinkemeier U., Weber K. Purification and physical properties of nematode mini-titins and their relation to twitchin. J Cell Sci. 1991 Apr;98(Pt 4):491–496. doi: 10.1242/jcs.98.4.491. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Nave R., Weber K. A myofibrillar protein of insect muscle related to vertebrate titin connects Z band and A band: purification and molecular characterization of invertebrate mini-titin. J Cell Sci. 1990 Apr;95(Pt 4):535–544. doi: 10.1242/jcs.95.4.535. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Olson N. J., Pearson R. B., Needleman D. S., Hurwitz M. Y., Kemp B. E., Means A. R. Regulatory and structural motifs of chicken gizzard myosin light chain kinase. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1990 Mar;87(6):2284–2288. doi: 10.1073/pnas.87.6.2284. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rasmussen U. B., Basset P., Daniel J. Y. Direct amplification of cDNA inserts from lambda libraries using the cloning-adapter as primer for PCR. Nucleic Acids Res. 1989 Apr 25;17(8):3308–3308. doi: 10.1093/nar/17.8.3308. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Roush C. L., Kennelly P. J., Glaccum M. B., Helfman D. M., Scott J. D., Krebs E. G. Isolation of the cDNA encoding rat skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Sequence and tissue distribution. J Biol Chem. 1988 Jul 25;263(21):10510–10516. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Saiki R. K., Scharf S., Faloona F., Mullis K. B., Horn G. T., Erlich H. A., Arnheim N. Enzymatic amplification of beta-globin genomic sequences and restriction site analysis for diagnosis of sickle cell anemia. Science. 1985 Dec 20;230(4732):1350–1354. doi: 10.1126/science.2999980. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Sanger F., Nicklen S., Coulson A. R. DNA sequencing with chain-terminating inhibitors. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1977 Dec;74(12):5463–5467. doi: 10.1073/pnas.74.12.5463. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Shoemaker M. O., Lau W., Shattuck R. L., Kwiatkowski A. P., Matrisian P. E., Guerra-Santos L., Wilson E., Lukas T. J., Van Eldik L. J., Watterson D. M. Use of DNA sequence and mutant analyses and antisense oligodeoxynucleotides to examine the molecular basis of nonmuscle myosin light chain kinase autoinhibition, calmodulin recognition, and activity. J Cell Biol. 1990 Sep;111(3):1107–1125. doi: 10.1083/jcb.111.3.1107. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Staros J. V., Wright R. W., Swingle D. M. Enhancement by N-hydroxysulfosuccinimide of water-soluble carbodiimide-mediated coupling reactions. Anal Biochem. 1986 Jul;156(1):220–222. doi: 10.1016/0003-2697(86)90176-4. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Moffatt B. A. Use of bacteriophage T7 RNA polymerase to direct selective high-level expression of cloned genes. J Mol Biol. 1986 May 5;189(1):113–130. doi: 10.1016/0022-2836(86)90385-2. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Studier F. W., Rosenberg A. H., Dunn J. J., Dubendorff J. W. Use of T7 RNA polymerase to direct expression of cloned genes. Methods Enzymol. 1990;185:60–89. doi: 10.1016/0076-6879(90)85008-c. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Takio K., Blumenthal D. K., Walsh K. A., Titani K., Krebs E. G. Amino acid sequence of rabbit skeletal muscle myosin light chain kinase. Biochemistry. 1986 Dec 2;25(24):8049–8057. doi: 10.1021/bi00372a038. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Tokuyasu K. T., Maher P. A. Immunocytochemical studies of cardiac myofibrillogenesis in early chick embryos. I. Presence of immunofluorescent titin spots in premyofibril stages. J Cell Biol. 1987 Dec;105(6 Pt 1):2781–2793. doi: 10.1083/jcb.105.6.2781. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Trinick J., Knight P., Whiting A. Purification and properties of native titin. J Mol Biol. 1984 Dec 5;180(2):331–356. doi: 10.1016/s0022-2836(84)80007-8. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Wang K., Wright J. Architecture of the sarcomere matrix of skeletal muscle: immunoelectron microscopic evidence that suggests a set of parallel inextensible nebulin filaments anchored at the Z line. J Cell Biol. 1988 Dec;107(6 Pt 1):2199–2212. doi: 10.1083/jcb.107.6.2199. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Yanisch-Perron C., Vieira J., Messing J. Improved M13 phage cloning vectors and host strains: nucleotide sequences of the M13mp18 and pUC19 vectors. Gene. 1985;33(1):103–119. doi: 10.1016/0378-1119(85)90120-9. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]





