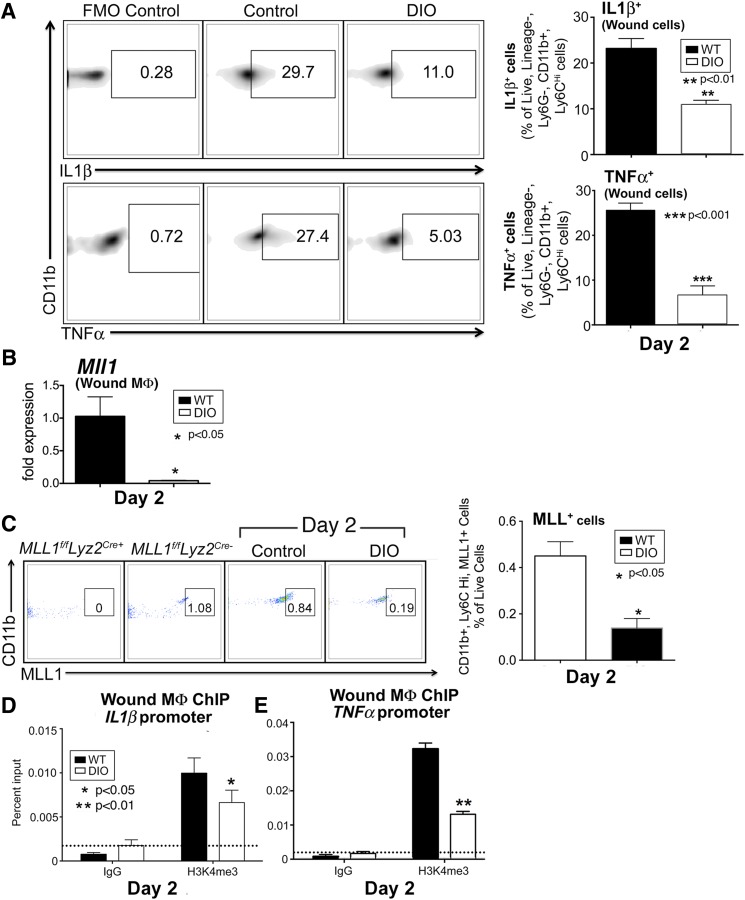
Figure 6.
Macrophages isolated from DIO mice display decreased early inflammatory cytokine production, MLL1, and H3K4me3 at inflammatory gene promoters. A: DIO and control murine wounds were harvested 2 days after injury, and wound cells were isolated. Single-cell suspensions were processed for flow cytometry. Density plots and associated data for IL-1β and TNF-α staining in live, lineage−, Ly6G−, CD11b+, Ly6CHi cells (as gated in Fig. 4) from DIO and control wounds (n = 12, repeated one time). B: DIO and control wounds were harvested 2 days after injury for cell isolation and macrophage selection for CD11b+[CD3−, CD19−, Ly6G−] cells through MACS. MLL1 expression as measured by qPCR from wound macrophages (n = 14, repeated one time). C: Pseudocolor plots and data analysis of wound MLL1+, CD11b+, Ly6CHi cells as a percentage of live cells in control and DIO mice at day 2 postinjury. Mll1f/fLyz2Cre+ and littermate control spleens were used as staining controls for MLL1 (n = 10; repeated one time). D and E: DIO and control wounds were harvested 2 days after wounding for cell isolation and macrophage selection for CD11b+[CD3−, CD19−, Ly6G−] cells through MACS. ChIP analyses of wound macrophages for H3K4me3 at the NF-κB binding sites of the promoters of IL1β (D) and TNFα (E) were performed (n = 12, repeated two times). Statistical analysis was by Student t test. Data are mean ± SEM. FMO, fluorescence minus one; MΦ, macrophage; WT, wild type.