Fig. 3.
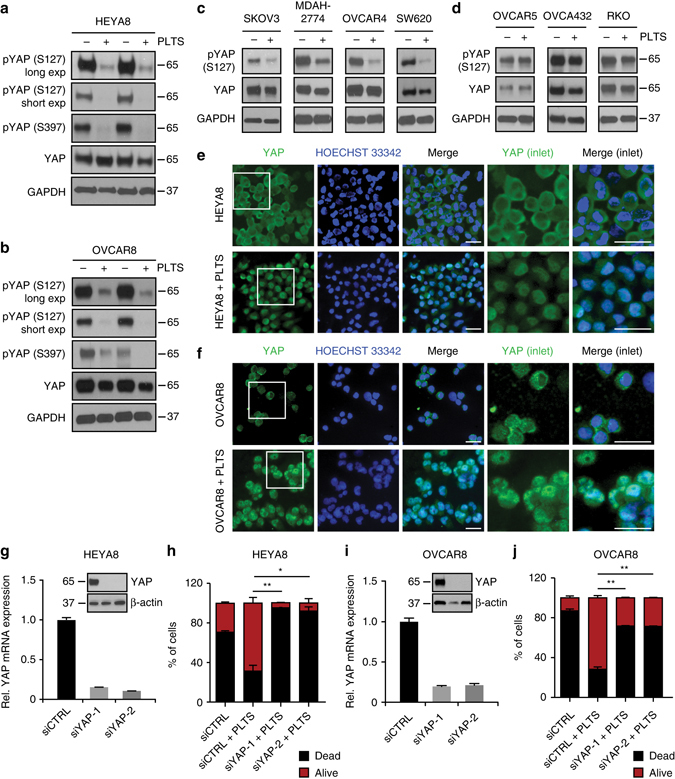
YAP1 is activated by platelets and is indispensable for platelet-induced anoikis resistance. a, b Western blot analysis of phosphorylated YAP1 (S127 and S397) and total YAP1 in HEYA8 a and OVCAR8 b cells after two hours under low-attachment conditions with or without platelet co-incubation. GAPDH was used as a loading control (n = 5). c, d Western blot analysis of phosphorylated YAP1 (S127) and total YAP1 in SKOV3, MDAH-2774, OVCAR4, SW620 c and OVCAR5, OVCA432 and RKO d GAPDH was used as a loading control (n = 3). e, f Immunofluorescence staining of YAP1 in HEYA8 e and OVCAR8 f cells after two hours under low-attachment conditions with (lower panels) or without (upper panels) platelet co-incubation. Inlets showing higher magnification of cells on the right side of the panels. Nuclear counterstain was done using Hoechst 33342 (n = 3). Scale bars = 20 µm. g QRT–PCR and western blot analysis in HEYA8 cells showing efficiency of YAP1 knockdown on the RNA and protein level using two different siRNAs (n = 3). h Bar graphs showing number of dead (SYTOX Red positive, black) and living (SYTOX Red negative, red) HEYA8 cells after 72 h of low attachment and 96 h after siRNA transfection (n = 3, two-sided Student’s t-test). i QRT–PCR and western blot analysis in OVCAR8 cells showing efficiency of YAP1 knockdown on the RNA and protein level using two different siRNAs (n = 3). j Bar graphs showing number of dead (SYTOX Red positive, black) and living (SYTOX Red negative, red) OVCAR8 cells after 72 h of low attachment and 96 h after siRNA transfection (n = 3, two-sided Student’s t-test). Bars and error bars represent mean values and the corresponding SEMs (*p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, ***p < 0.001)
