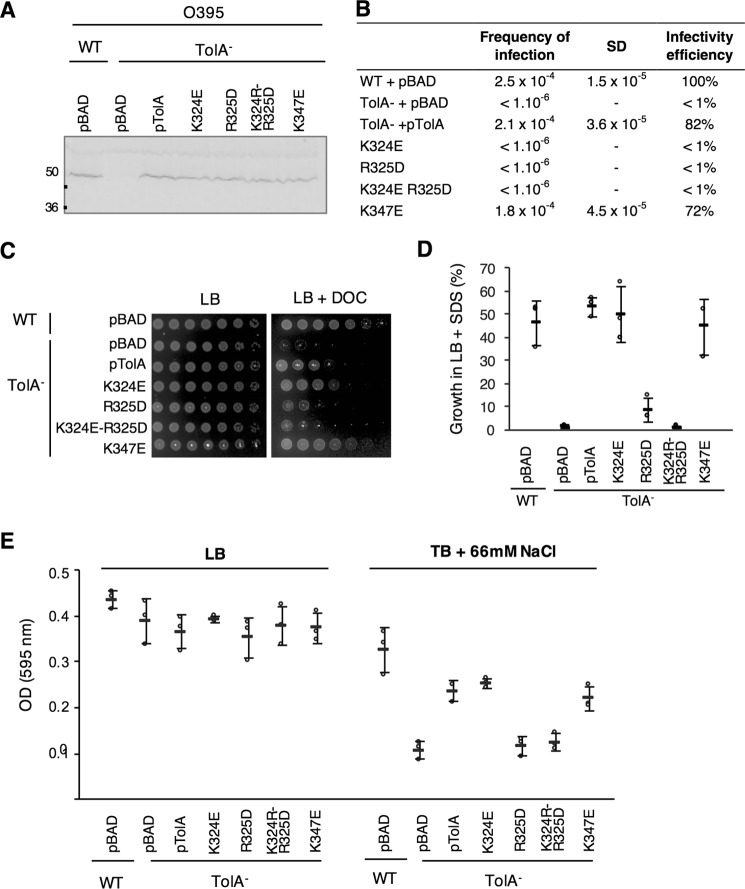
Figure 6.
Phenotypic characterization of V. cholerae O395 WT and TolA− strains complemented with TolA variants of interest. A, expression of the different pBAD-TolAVc constructs in V. cholerae was assessed by Western immunoblotting. A total of 0.3 absorbance units of whole-cell lysate were loaded onto an SDS-13.5% acrylamide gel and immunodetected using polyclonal antibody raised against E. coli TolA. B, CTX transduction assays were conducted in triplicate, and CFU were counted on LB or LB supplemented with Cm. Frequency of infection is calculated by dividing the number of transductants (CmR colonies) by the number of O395 recipients. The mean and the standard deviation of the triplicate is presented. For each construct, infection efficiency is expressed as the percentage of infection compared with the receiver strain carrying the empty vector. C, membrane integrity assay. 4 μl of 5-fold dilution of normalized cultures (initial A600 = 1) were spotted on LB+kanamycin plates alone or supplemented with 1% DOC. D, percentage of survival to SDS-0.125% of the different strains compared with V. cholerae WT strain carrying an pBAD empty vector. For each strain, percentage of growth is calculated as A600 nm of each stain grown in LB+SDS × 100/A595 nm of the WT strain carrying an empty vector and grown in LB. E, quantification of V. cholerae O395 WT and TolA− mutant growth in LB (407 mosm) and in tryptone broth (TB) supplemented with 66 mm NaCl (123 mosm). The experiment was conducted in triplicate, and the error bars report standard deviations.