Figure 7.
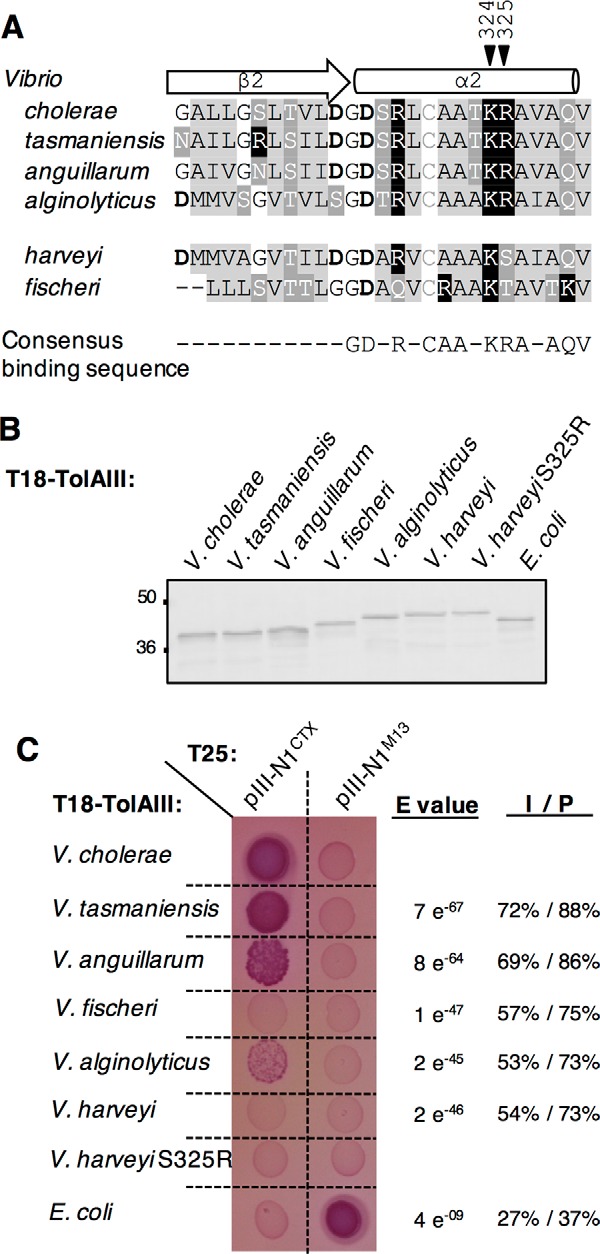
Conservation of TolA Lys-324 and Arg-325 residues in other Vibrio species. A, sequence alignment between V. cholerae, V. tasmaniensis, V. anguillarum, V. alginolyticus, V. harveyi, and V fischeri TolAIII β2-α2 domain. Residues are colored as follows: basic (black squares), acidic (bold), hydrophobic (light gray),and polar uncharged (dark gray). Black arrowheads point the Lys-324–Arg-325 motif. B, Western immunoblot of 0.2 absorbance units of whole-cell lysates of E. coli DH5α strain carrying T18-TolAIII construct from selected Vibrionaceae and from E. coli and probed with anti-Cya antibody. The molecular mass markers (in kDa) are indicated on the left. C, T18-TolAIII constructs from selected species were tested for their binding ability to the T25-pIII-N1CTX in an Oxi-BTH assay on MacConkey plates. E. coli TolAIII and pIII-N1M13 are used as a controls. Sequence comparison between each TolAIII of interest and the V. cholerae TolAIII amino acid sequences using Blast2 is reported on the right of the panel as E value, identity (I) and positive (P) values.
