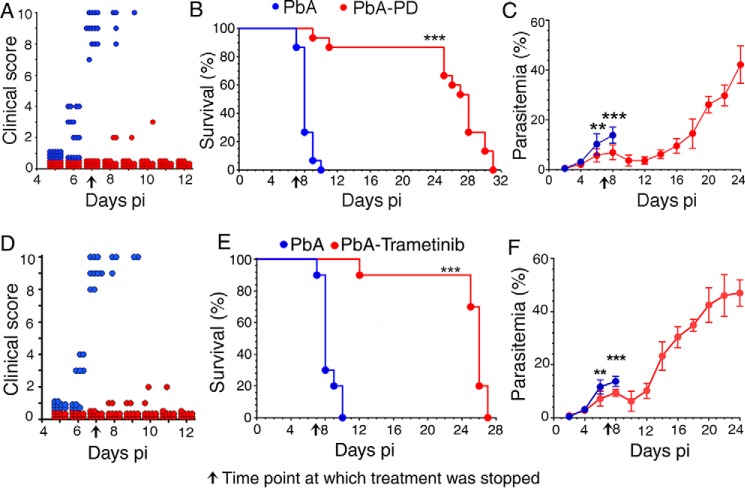
Figure 2.
MEK1/2 inhibitor treatment controls malaria parasitemia and prevents ECM pathogenesis. PbA-infected mice (n = 15/group) were treated i.p. with 3 mg of PD/kg body weight or vehicle daily starting at 6 h pi. In separate experiments, PbA-infected mice (n = 10 mice/group) were treated orally with either vehicle or 5 mg of trametinib/kg body weight daily starting at 6 h pi. CM symptoms, parasitemia, and survival rates were assessed. Plots of CM clinical scores (A and D), survival rates (B and E), and parasitemia (C and F) are shown. The arrow in each panel indicates the time point (7 days pi) at which inhibitor treatment was stopped. PbA, vehicle-treated infected mice; PbA-PD, PD-treated infected mice; PbA-Trametinib, trametinib-treated infected mice. Mice survival data (B and E) were analyzed by log–rank (Mantel–Cox) test, and parasitemia results (C and F) were analyzed by unpaired two-tailed t test. Error bars, S.D. **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.