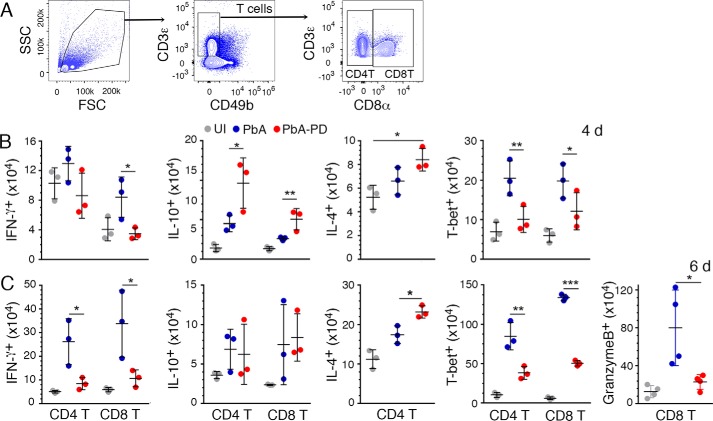
Figure 9.
Treatment with MEK1/2 inhibitor suppresses malaria-induced Th1 development and CD8+ T cell cytotoxicity. PbA-infected mice were treated i.p. with 3 mg of PD/kg body weight or vehicle daily starting at 6 h pi. Spleen cells from the PbA-infected mice at 4 days and 6 days pi were stained with antibodies against surface markers and the indicated intracellular proteins and analyzed by flow cytometery. A–C, shown are the gating strategy for CD4+ and CD8+ T cells (A) and IFNγ+, IL-10+, IL-4+, T-bet+, and granzyme B+ CD4+ and/or CD8+ T cell numbers per spleen (B and C). The cytokine+, T-bet+, and granzyme B+ cells were gated as shown supplemental Fig. S4, A and B. The data are representative of three or four independent experiments; n = 3 or 4 mice/group in each experiment. Statistical analysis was by one-way ANOVA with Newman–Keuls correction for multiple comparisons. Error bars, S.D. *, p < 0.05; **, p < 0.01; ***, p < 0.001.