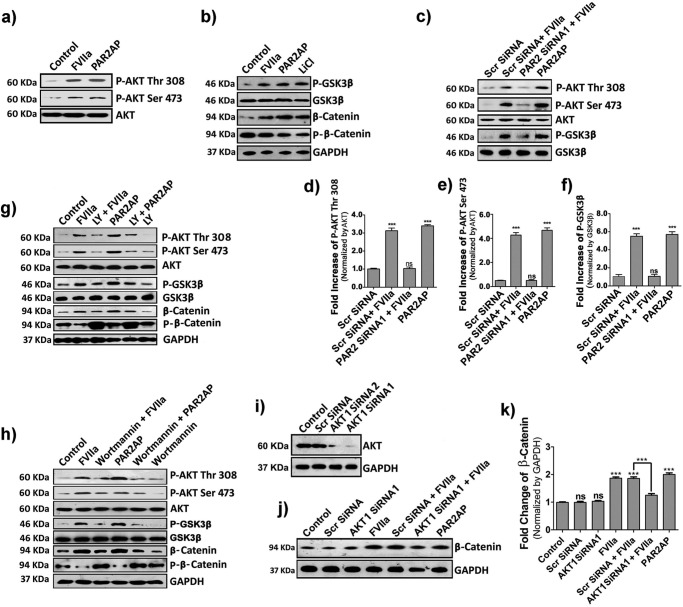
Figure 4.
TF-FVIIa or PAR2AP modulates β-catenin accumulation in MDA-MB-231 cells via AKT/GSK3β-dependent pathway. a, AKT phosphorylation (both at Thr-308 and Ser-473) at 10 min. b, cells were challenged with FVIIa, PAR2AP, and the positive control LiCl (40 mm), and the phosphorylation status of GSK3β (at Ser-9) and β-catenin and phospho-β-catenin levels were checked at 1, 4, and 4 h, respectively by Western blotting. c, phospho-AKT (at Thr-308 and Ser-473) and -GSK3β (at Ser-9) were checked in PAR2 siRNA1- and scrambled (Scr) siRNA-treated cells after challenging with FVIIa. d, e, and f, quantitative band intensities of phospho-AKT at Thr-308 and Ser-473 and phospho-GSK3β at Ser-9 normalized by respective proteins were measured using ImageJ and GraphPad Prism 5. Cells were treated with either LY294002 (20 μm) (g) or wortmannin (50 μm) (h) 1 h before FVIIa or PAR2AP treatment, and the cell lysates were analyzed for phospho-AKT (both at Thr-308 and Ser-473), phospho-GSK3β (at Ser-9), β-catenin, and phospho-β-catenin by Western blotting. i, AKT1 knockdown was performed by two siRNAs (1 and 2) and analyzed by Western blotting. j, β-catenin levels were estimated in scrambled and AKT1 knockdown cells after FVIIa treatment by Western blotting. k, accumulated β-catenin levels (normalized by GAPDH) were quantified using ImageJ and GraphPad Prism 5. Error bars represent ±S.E. of the mean. ***, p < 0.001; ns, non-significant using Student's t test; n = 3.