Figure 3.
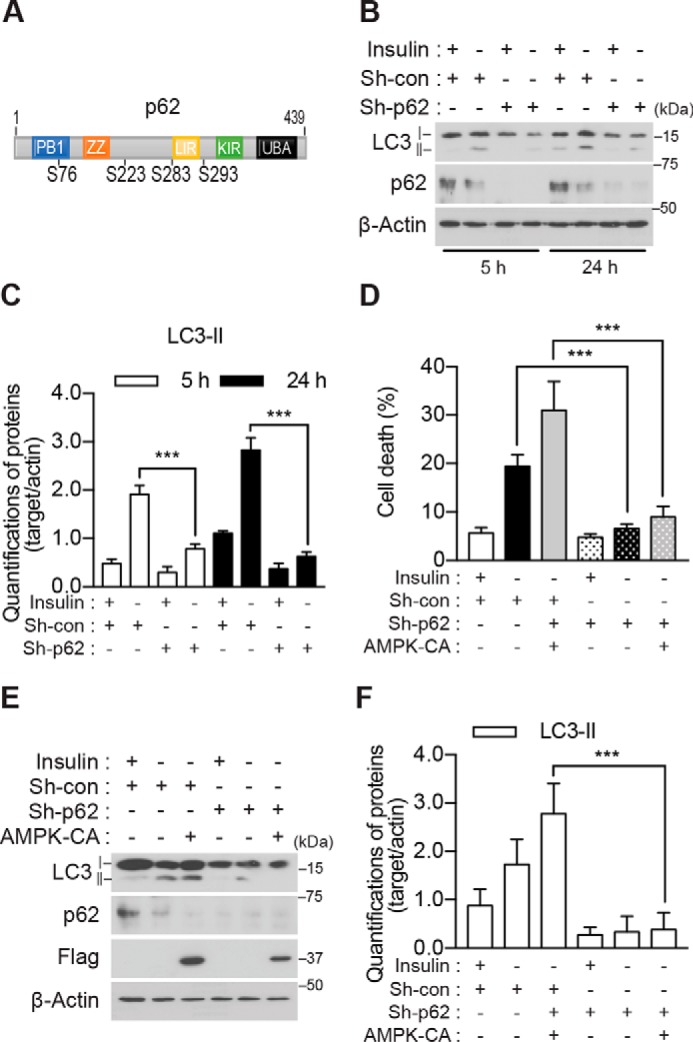
p62 is required for ACD in I(−) HCN cells. A, schematic representation of the functional domains and predicted AMPK α2 phosphorylation sites of p62. B, knockdown of p62 abrogated an increase in LC3-II following insulin withdrawal. C, quantification of LC3-II after normalization to β-actin (n = 3). D, p62 knockdown attenuated the AMPK-CA-induced increase in cell death I(−) HCN cells (n = 6). E, p62 knockdown attenuated the AMPK-CA-induced increase in LC3-II in I(−) HCN cells. F, quantification of LC3-II after normalization to β-actin (n = 6). Error bars represent ±S.D. from independent assays. ***, p < 0.001. con, control; ZZ, ZZ-type zinc finger domain; LIR, LC3-interacting region; UBA, ubiquitin-associated domain; KIR, Keap1-interacting region.
