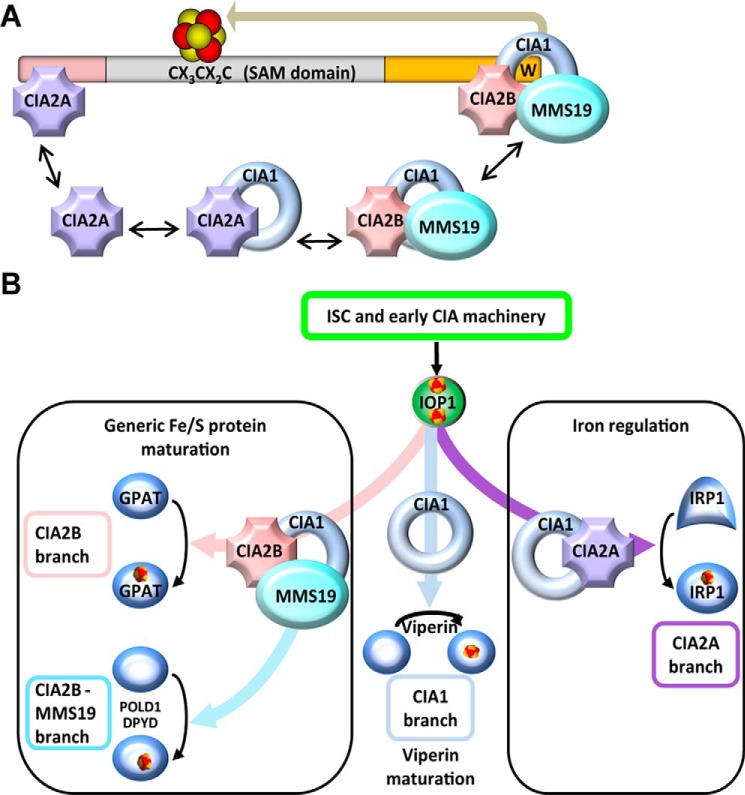
Figure 6.
Model for the mode of interaction of CIA-targeting factors with viperin and for the unique maturation pathway. A, multimeric CIA-targeting complexes are present in the cell. As shown here, the CIA1–CIA2B–MMS19 complex interacts with the C terminus of viperin via direct contacts of both CIA1 and CIA2B. The two factors in turn recruit MMS19 to viperin. CIA2A binds at the N terminus of viperin and is stabilized by CIA1. Insertion of the radical SAM Fe/S cluster in the middle domain is mediated by C-terminally bound CIA1 only (see Ref. 6 and this study). B, Fe/S cluster maturation of viperin represents a novel branch of the CIA pathway that is initiated by the mitochondrial ISC machinery, early-acting CIA components, and IOP1 (20, 21). The components of the CIA1–CIA2B–MMS19-targeting complex operate in various combinations to facilitate Fe/S cluster insertion into dedicated client proteins, including GPAT, POLD1, and DPYD. CIA2A is specifically required for the maturation of IRP1 thus affecting cellular iron homeostasis and is stabilized by binding to CIA1. In contrast to all other known client Fe/S proteins, CIA1 appears to mediate Fe/S cluster insertion into the radical SAM protein viperin independently of the other CIA-targeting factors, thus representing a minimal requirement for CIA proteins.