Figure 4.
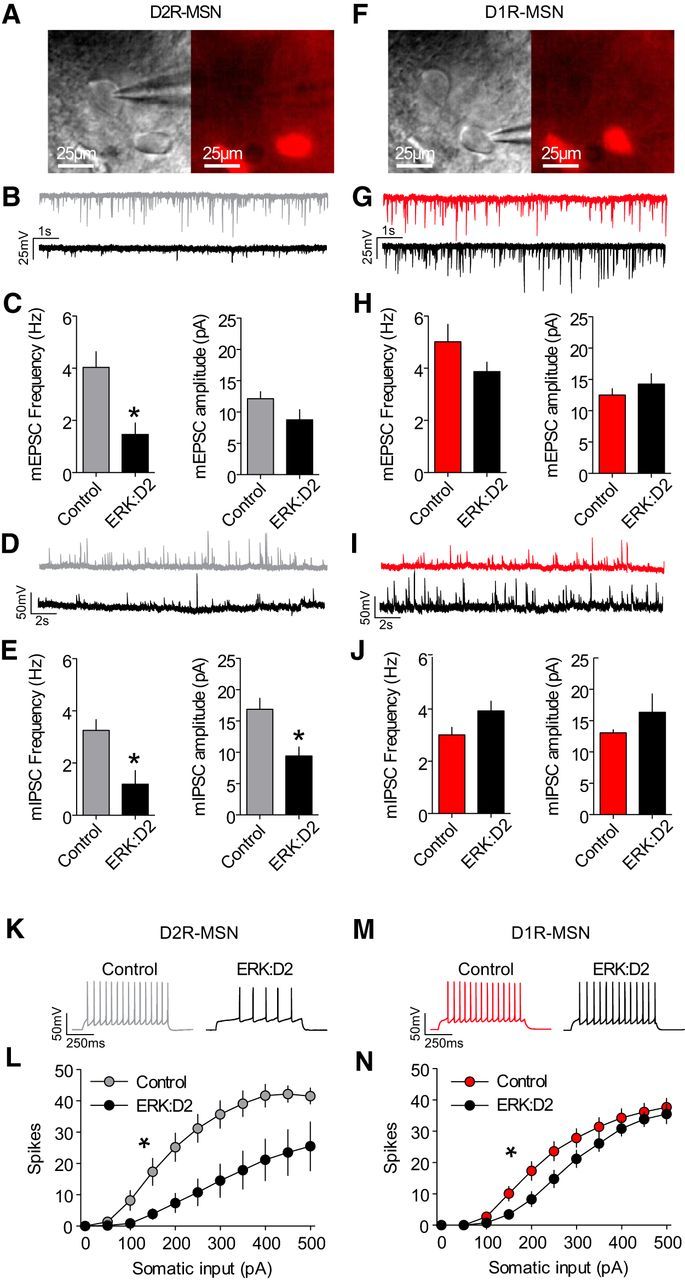
Markedly reduced excitability of ERK-deleted D2R-MSNs. A, Image of pipette recording from a D2R-MSN negative for D1tdTomato (red). B, Representative mEPSC recordings of D2R-MSNs from control (gray) and ERK:D2 mutant (black) mice. C, Summary of mEPSC frequencies and amplitudes from control (gray; n = 3 mice, n = 10 neurons) and ERK:D2 mutant (black; n = 3 mice, n = 8 neurons) D2R-MSNs. mEPSC frequency is significantly reduced in ERK:D2 mutant D2R-MSNs (*p < 0.01), whereas mEPSC amplitude is unchanged. D, Representative mIPSC recordings of D2R-MSNs from control (gray) and ERK:D2 mutant (black) mice. E, Summary of mIPSC frequencies and amplitudes from control (gray; n = 3 mice; n = 10 neurons) and ERK:D2 mutant (black; n = 3 mice; n = 7 neurons) D2R-MSNs. Both mIPSC frequency and amplitude are reduced significantly in ERK:D2 mutant D2-MSNs (*p < 0.01). F, Representative image of recording pipette in a D1tdTomato-positive (red) D1R-MSN. G, Representative mEPSC recordings of D1R-MSNs from control (red) and ERK:D2 mutant (black) mice. H, Summary of mEPSC frequencies and amplitudes from control (red; n = 3 mice; n = 8 neurons) and ERK:D2 mutant (black; n = 3 mice; n = 7 neurons) D1R-MSNs. There is no significant change in mEPSC frequency or amplitude in ERK:D2 mutant D1R-MSNs compared with control. I, Representative mIPSC recordings of D1R-MSNs from control (red) and ERK:D2 mutant (black) mice. J, Summary of mIPSC frequencies and amplitudes from control (red; n = 3 mice; n = 8 neurons) and ERK:D2 mutant (black; n = 3 mice; n = 7 neurons) D1R-MSNs. There is no significant difference between ERK:D2 mutant D1R-MSNs and control MSNs. K, Representative traces of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from D2R-MSNs in control (gray) and ERK:D2 mutant (black) mice. L, Relationship between elicited action potential responses and somatic current injection in D2R-MSNs of control (gray; n = 3 mice; n = 9 neurons) and ERK:D2 mutant (black; n = 3 mice; n = 10 neurons) mice. D2R-MSNs from ERK:D2 mutant mice have a significantly reduced capacity to elicit action potentials (*p < 0.001). M, Representative traces of whole-cell patch-clamp recordings from D1R-MSNs in control (red) and ERK:D2 mutant (black) mice. N, Relationship between elicited action potential responses and somatic current injection in D1R-MSNs of control (red; n = 3 mice; n = 9 neurons) and ERK:D2 mutant (black; n = 3 mice; n = 9 neurons) mice. Intrinsic excitability in D1R-MSNs of ERK:D2 mutant mice was slightly, but significantly, reduced compared with controls (*p < 0.01).
