Figure 6.
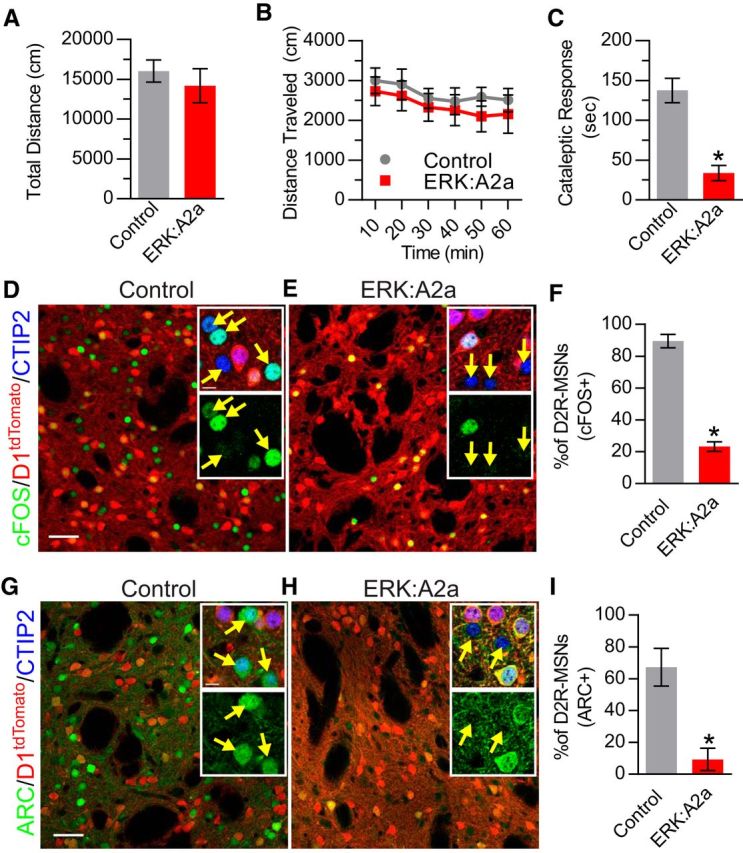
Basal and haloperidol-induced behavioral and gene expression changes in ERK:A2a mice. A, B, Open-field locomotor testing of ERK:A2a and control mice (n = 7 animals/genotype). A, There is no significant difference in cumulative distance traveled (1 h test) between ERK:A2a mutant and control littermates. B, Total distance traveled as a function of time. No differences are observed between mutant and control animals. C, Cataleptic response 1 h after haloperidol administration (1 mg/kg). ERK:A2a mutant mice have a significantly reduced cataleptic response compared with littermate controls (*p < 0.001; n = 6 mice/genotype). D, E, Immunohistochemical labeling of activity-induced gene expression 1 h after haloperidol administration. All MSNs are labeled with Ctip2 (blue). D1R-MSNs are distinguished from D2R-MSNs by their expression of D1tdTomato(red). c-FOS (green) is upregulated in D2R-MSNs of control (D) but not ERK:A2a mutant (E) mice. Insets show higher magnification of all three labels (top) and c-FOS only (bottom). D2R-MSNs are indicated by yellow arrows. F, Quantitative analysis showing a significant reduction in the percentage of D2R-MSNs expressing c-FOS in ERK:A2a mutant animals compared with control animals (*p < 0.001; n = 3 mice/genotype; 200–250 cells/mouse). G, H, ARC (green) is upregulated in D2R-MSNs (yellow arrows) in control (G) but not ERK:A2a mutant (H) animals. I, Quantitative analysis demonstrating a significant decrease in the percentage of D2R-MSNs that upregulate ARC in ERK:A2a mutant mice (*p < 0.05; n = 3 mice/genotype; 200–250 cells/mouse). All data are presented as mean ± SEM. Scale bars, 50 μm; inset, 20 μm.
