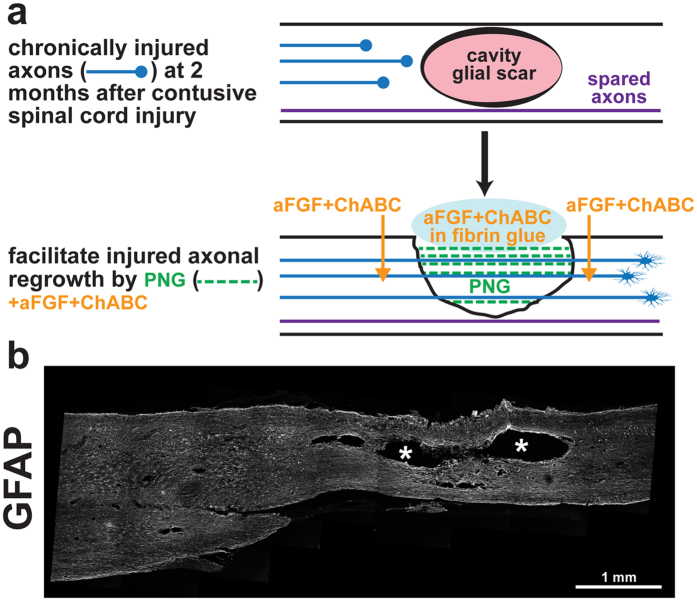
Figure 1.
Surgical intervention to bridge the gap after chronic contusive SCI. (a) Schematic diagram illustrating the repair strategy. At two months post-injury, a cystic cavity forms at the injury site (pink oval, top drawing). For repair surgery, the cavity is exposed via the dorsal cord surface, scar tissue lining the cavity is gently removed, and several autologous peripheral nerve segments (green dotted lines, bottom drawing) are longitudinally placed in the cavity to span the lesion. aFGF+ChABC (orange) is injected rostrally, caudally, and at the sides of the spinal cord adjacent to the graft. A glue made of aFGF, ChABC, and fibrin is used to stabilize the graft (blue oval, bottom drawing). (b) GFAP-stained spinal cord two months post-contusion. Note the large cavity in the epicenter of the injured site, as indicated by*.