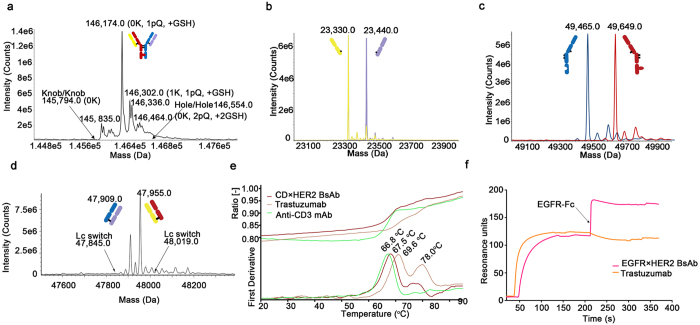
Figure 4.
Physico-chemical characterization of BsAbs (post-protein A purification). IMS Q-Tof mass spectrometry, Differential scanning fluorimetry and SPR were performed for BsAb (CD3×HER2). (a) Mass spectrometry analysis of the deglycosylated and non-reduced BsAb was performed to demonstrate correct mass for the product without mispairing. Expected mass location for potential knob/knob (K/K), and hole/hole (H/H) homodimers were labeled by the arrows. K, C-terminal lysine presence; pQ, N-terminal pyroglutamic acid cyclization; +GSH, reduced glutathione addition. (b,c) Mass spectrometry analysis of the deglycosylated and reduced sample to confirm the presence of two different light chains and two different heavy chains. (d) Mass spectrometry analysis of the papain digested sample to determine if light chain switching occurred during the BAPTS process. The arrows indicate theoretical masses for the Fab if cognate heavy-light chain pairs had switched. (e) Differential scanning fluorimetry measurement of the BsAb (CD3×HER2) and it’s parental mAbs. (i) Dual antigen binding behavior of the BsAb (EGFR×HER2) measured by SPR. The BsAb was injected over a surface containing immobilized HER2-Fc antigen followed by injection of EGFR-Fc. Trastuzumab was used as a control.