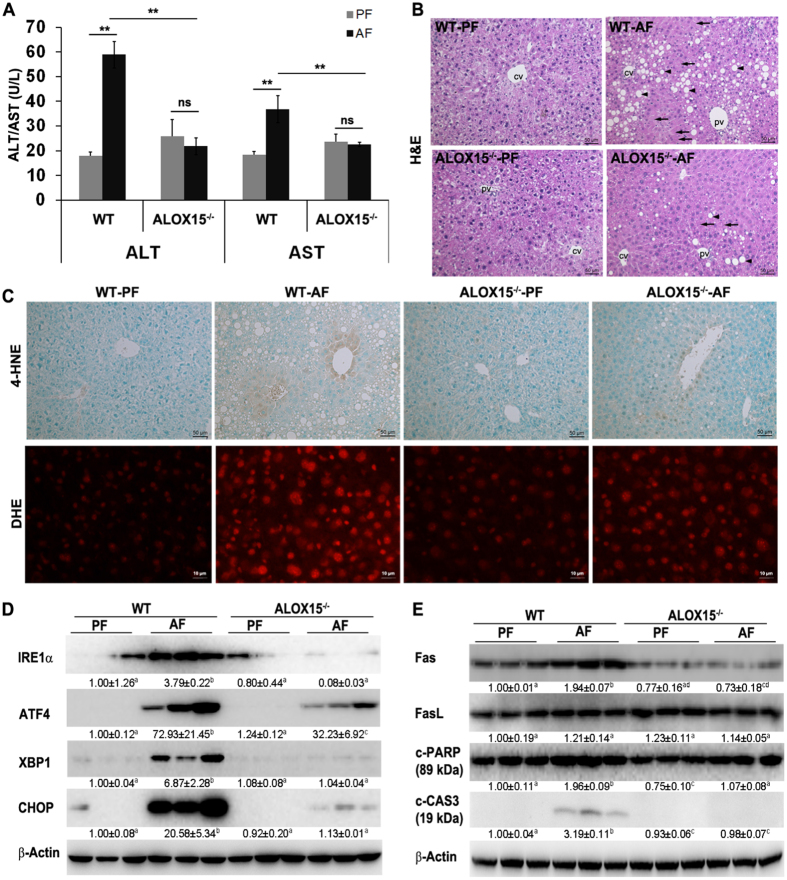
Figure 4.
ALOX15 knockout attenuated alcohol-induced liver injury, ROS production, ER stress, and apoptosis. WT and ALOX15−/− male mice were fed with control (PF) or alcohol (AF) liquid diet for 8 weeks. (A) Plasma ALT and AST. (B) Liver histopathological changes shown by H&E staining (arrows: necrosis, arrowheads: lipid droplets). (C) Representative images of 4-HNE staining (upper panel) and DHE staining (lower panel). (D) Immunoblot of proteins involved in ER stress. (E) Immunoblot of proteins involved in apoptosis. Protein levels were quantitated by NIH image J. All values are denoted as means ± SD (n = 6 in A, n = 3 in D and E). Significant differences were indicated by different letters (ANOVA, P < 0.05). *P < 0.05, **P < 0.01, ns, not significant (t-test). H&E: hematoxylin and eosin staining, 4-HNE: 4-hydroxynonenol, DHE: Dihydroethidium, CV: central vein, PV: portal vein.