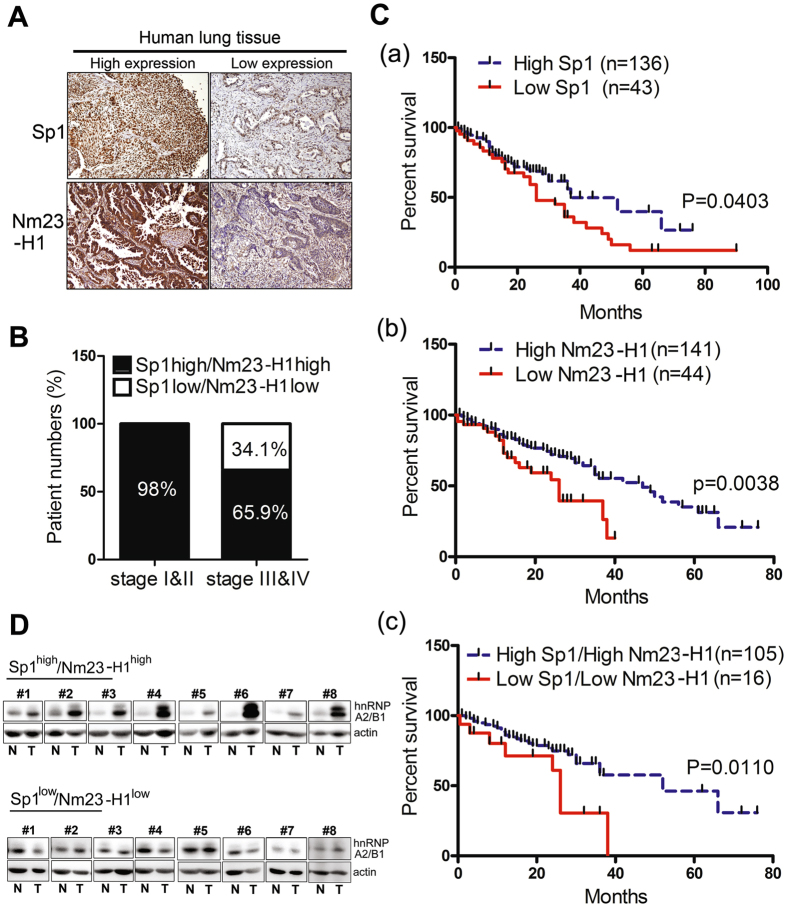
Figure 2.
The relevance between Sp1/Nm23-H1 levels and the prognosis of lung cancer patients. (A) Samples from lung cancer patients were prepared for IHC staining with antibodies against Sp1 and Nm23-H1. (B) After IHC staining samples from 179 patients with anti-Sp1 antibodies and 185 patients with anti-Nm23-H1 antibodies, the relationship between Sp1/Nm23-H1 levels and the stage of lung cancer of the patients was analyzed. (C) The survival rate was analyzed between patients with higher Sp1 or lower Sp1 expression (a), patients with higher Nm23-H1 or lower Nm23-H1 expression (b), and between patients with higher Sp1/Nm23-H1 or lower Sp1/Nm23-H1 expression (c) by Kaplan–Meier analysis. The P-value was determined by a two-sided log-rank test. (D). The level of hnRNPA2/B1 in the clinical samples with high levels of Sp1 and Nm23-H1 or with low levels of Sp1 and Nm23-H1 was studied by Western blotting with anti-hnRNPA2/B1 antibodies.