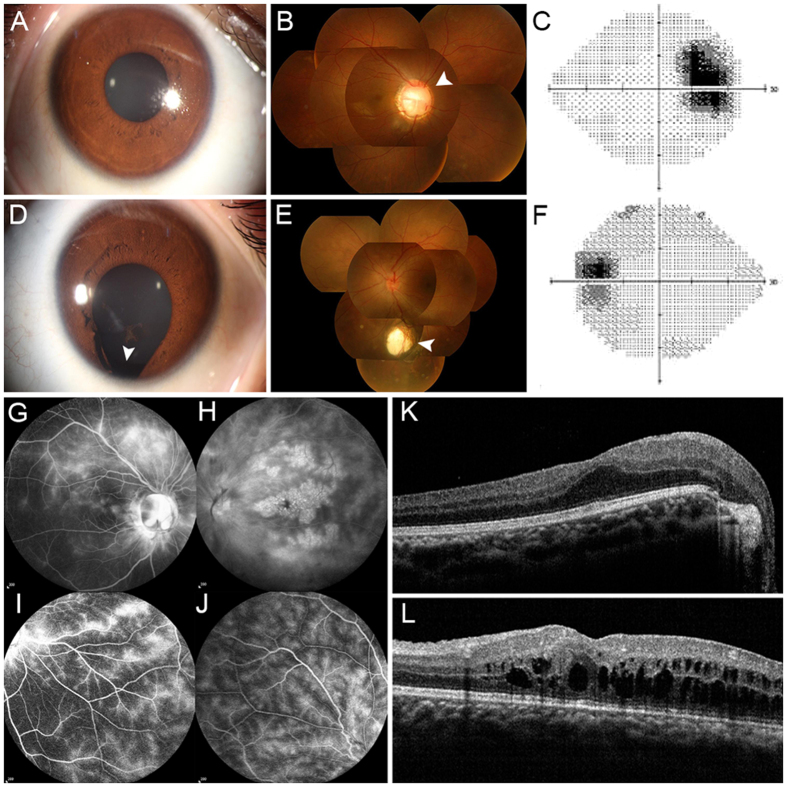
Figure 1.
Clinical features of the patient with RAX mutation. (A and D) Representative photographs of the anterior segments. (A) The normally-performing right eye. (D) The left eye presented with iris coloboma located inferiorly (as indicated by the white arrow). (B and E) Fundus photographs showed optic disc coloboma in right fundus (white arrow) and choroid coloboma in the left fundus (white arrow). (C and F) Visual field test demonstrates a physiological blind spot and low visual contrast in the right eye. (G–J) FFA images revealed leakage of fluorescein from the macular and peripheral retinal telangiectatic vessels in both eyes with different degrees. (K and L) Spectral-domain optical coherence tomographic and visual field test. (K) Macular edema in the right eye. (L) Macular edema and retinoschisis in the left eye.