Figure 2.
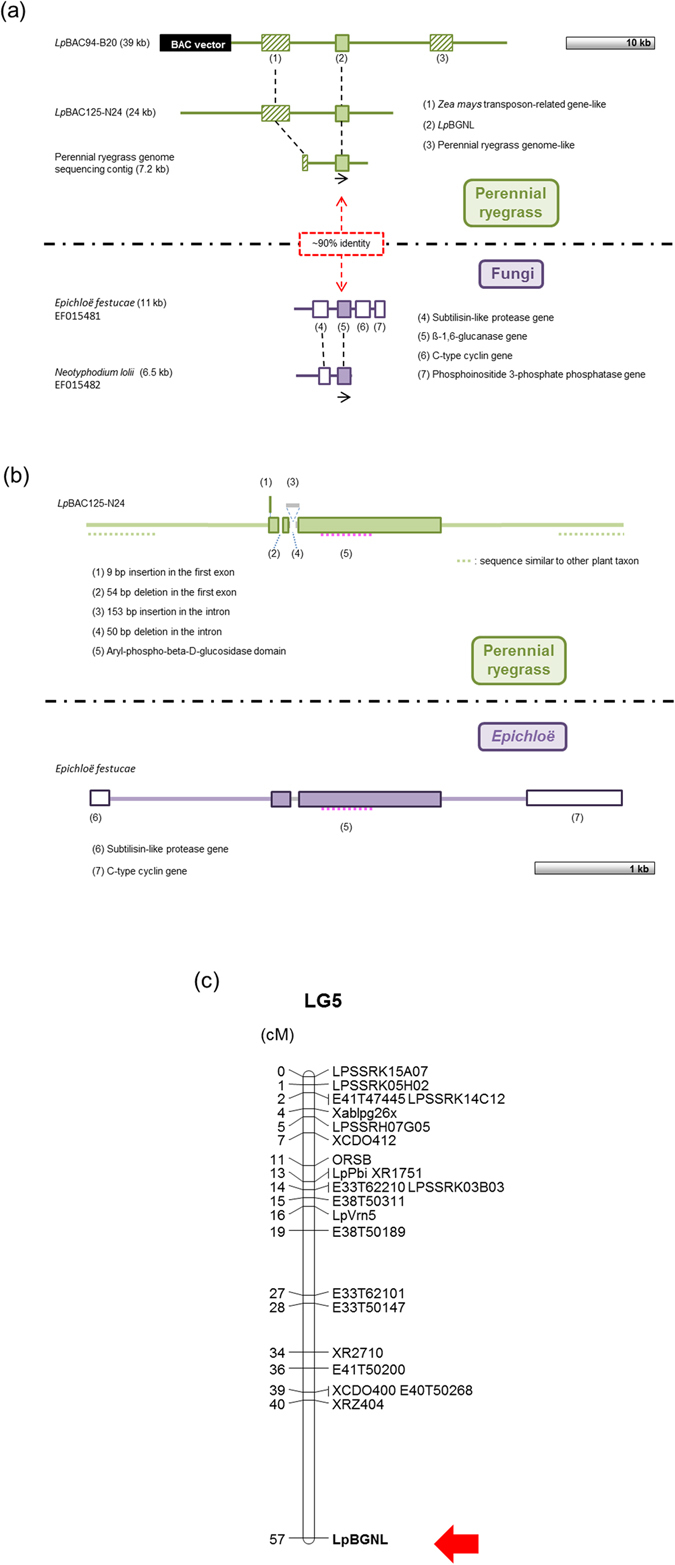
Genome structure of the LpBGNL and E. festucae ß-1,6-glucanase genes and genetic linkage analysis for LpBGNL. (a) Alignment of genome sequences from perennial ryegrass and Epichloë species. The light green-filled and striped boxes show the location of LpBGNL and the plant genome-related sequence, respectively. The black-filled box represents the BAC vector. The purple-filled and empty boxes show the location of the ß-1,6-glucanase gene and flanking gene, respectively. The transcription direction of the genes is indicated with the arrow. Corresponding gene sequences are connected with black dashed lines. (b) Alignment of coding regions of the LpBGNL and Epichloë ß-1,6-glucanase genes. The light green and purple lines represent non-gene coding region of perennial ryegrass and Epichloë species. The grey line and pink breaking line show the location of the intron and aryl-phospho-beta-D-glucosidase domain, respectively. (c) Genetic linkage map of perennial ryegrass LG5 with the LpBGNL-related locus. The LpBGNL-related marker locus is indicated with the red arrow. Genetic distance (cM) is shown on the right side of the genetic markers.
