Figure 2.
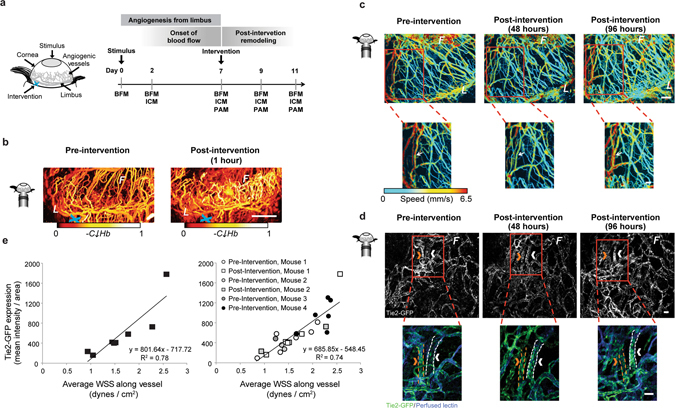
Surgical intervention caused a redistribution in blood flow that resulted in a quantifiable change in blood velocity, flow distribution, and Tie2-GFP fluorescence intensity over time throughout the network. (a) Schematic represents the corneal angiogenesis assay in which blood vessels grow from the limbus (“L”) into the avascular cornea, creating an angiogenic front (“F”). Surgical “intervention” (blue “x”) was performed by applying thermal cautery to an arteriole that feeds into from the limbus. (b) PAM images showing relative hemoglobin content (“CHb”) of corneal vessels pre-intervention and one hour post-intervention. (c) Dynamic changes in blood flow were visible using PAM in single capillary segments. Bottom row shows a magnified view of the regions boxed in red above. Changes in blood flow velocity (mm/s) are evident in individual vessel segments; white arrow indicates to one segment where flow speed was initially reduced and then returned to pre-intervention levels by 96 hours post-intervention. (d) Tie2-GFP fluorescence captured with ICM in single capillary segments over time. Bottom row shows a magnified view of the regions boxed in red above. Changes in Tie2-GFP fluorescence intensity within individual vessel segments are evident between time points. Arrows indicate the same vessel at each time point. Orange arrow indicates a vessel with decreased GFP fluorescence intensity at 96 hours post-intervention; white arrow indicates vessel with increased GFP fluorescence intensity 96 hours post intervention. In the bottom row, Tie2-GFP is green, and perfused IB4-isolectin is blue. (e) Vessels with higher WSS exhibited increased Tie2-GFP fluorescence intensity post-intervention. Data in graph on left are from vessels from two mice post-ligation (slope and R2 indicated); data in the graph on the right are from vessels assessed both pre- and post-ligation (slope and R2 indicated) from multiple mice. White scale bar indicates (b) 1 mm, (c,d) 50 µm.
