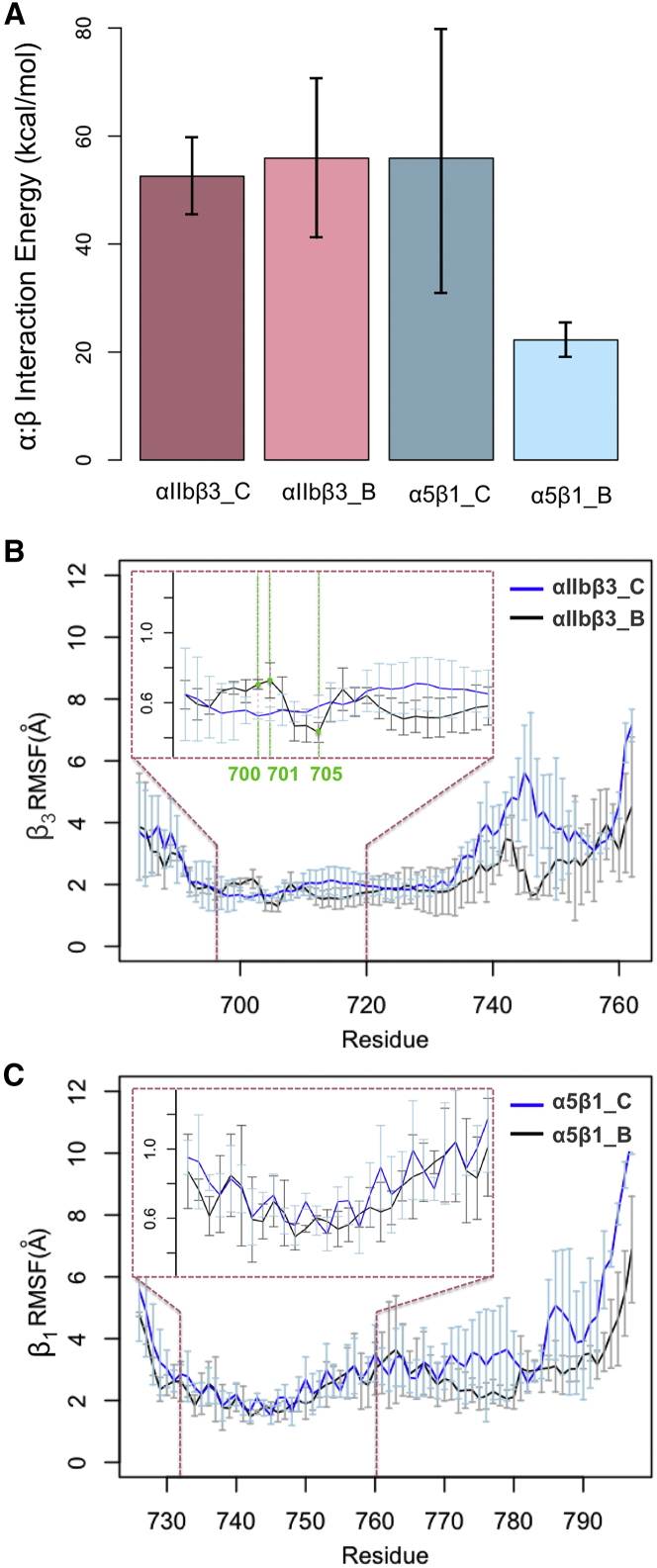
Figure 5.
The effect of cytoplasmic interactions on integrin activation. (A) The average energy between α5-β1 subunits in α5β1_B simulations is significantly decreased compared to that in α5β1_C simulations. Within the same simulation time, no change in the αIIb-β3 energy is observed upon α-actinin binding. (B) Atomic fluctuations are limited in the transmembrane domain relative to the cytoplasmic end of integrins in all simulations. The TMD regions are magnified in the insets. The RMSF of β3-tail is different between αIIbβ3_C and αIIbβ3_B simulations. Specifically, the error bars of atomic fluctuations do not overlap at residues 700, 701, and 705, which are all above residue 711 toward the extracellular side of TMD, showing a notable difference between the RMSF curves at those residues. (C) The RMSF of β1-TMD is similar between α5β1_C and αIIbβ3_B simulations. This most likely indicates that signal transmission through the β1-TMD is not significantly altered in the presence of α-actinin. To see this figure in color, go online.