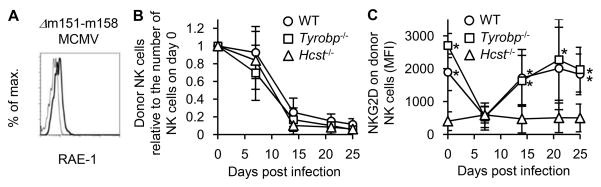
Figure 3. NK cells downregulate NKG2D after MCMV infection.
(A) Expression of RAE-1 proteins on C57BL/6 3T3 cells at 60 hours after infection with tissue culture-propagated Δm151-m158 MCMV at 1 PFU/cell. Thin and bold lines represent staining with an isotype-matched control and anti-RAE-1 pan-specific mAb. Data are representative of 2 experiments. (B–C) Two hundred thousand CD45.1+CD45.2+ WT NK cells, CD45.1+ Tyrobp−/− NK cells, and CD45.2+ Hcst−/− NK cells were co-transferred into DAP10- and DAP12-double deficient mice and infected with 1 x 105 PFU tissue culture-propagated Δm151-m158 MCMV. Donor WT NK cells and Tyrobp−/− NK cells were detected by expression of CD45 congenic markers and donor Hcst−/− NK cells were detected by expression of Ly49H and CD45 congenic markers. (B) The kinetics of the absolute number of donor NK cells in the blood are represented as the ratio relative to the number of donor NK cells in the blood on day 0 (before infection). (C) Expression of NKG2D on donor NK cells in the blood is represented as mean fluorescent intensity (MFI). Data were pooled from 2 experiments (n = 8 mice). *p <0.05.