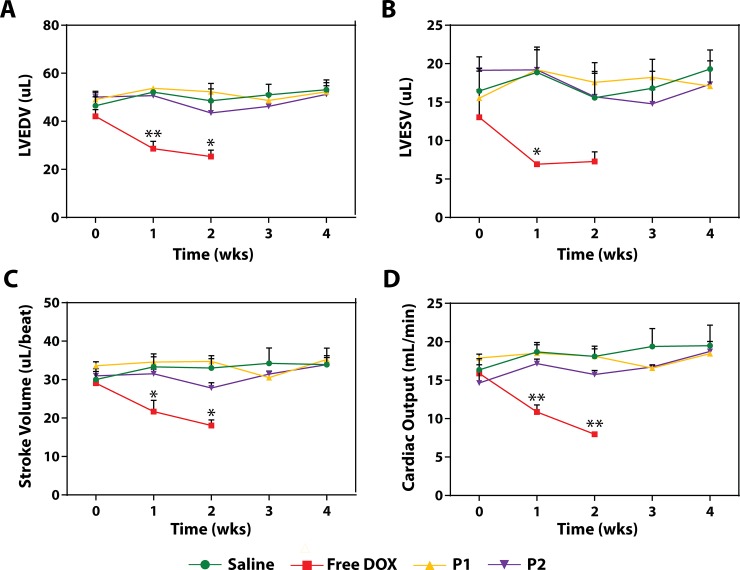
Fig 6. P1- and P2-mediated delivery of DOX escapes cardiotoxicity associated with free DOX administration.
We measured the cardiac function of mice undergoing treatment by saline, P1, P2, or free DOX. Results show the effects of each treatment on the (A) left ventricular end diastolic volume (LVEDV), (B) left ventricular end systolic volume (LVESV), (C) stroke volume (SV = LVEDV–LVESV), and (D) cardiac output (SV*heart rate). The statistically significant decrease in cardiac function by all four metrics is obvious already after Week 1 of free DOX treatment, while P1 and P2 particles do not induce any toxicity compared to the control. Further, free DOX mice had a 100% death rate by day 15, while P1- and P2-treated had a 100% survival rate during the monitoring period. Results are presented as a mean of three replicates ± SEM. Two-way ANOVA was used to test the statistical significance between P1, P2, and free DOX compared to the saline group, except for the free DOX group at Week 2, where a t-test was used because mice numbers did not match due to death in the free DOX group. Significance is denoted by * for p<0.05 and ** for p<0.01.