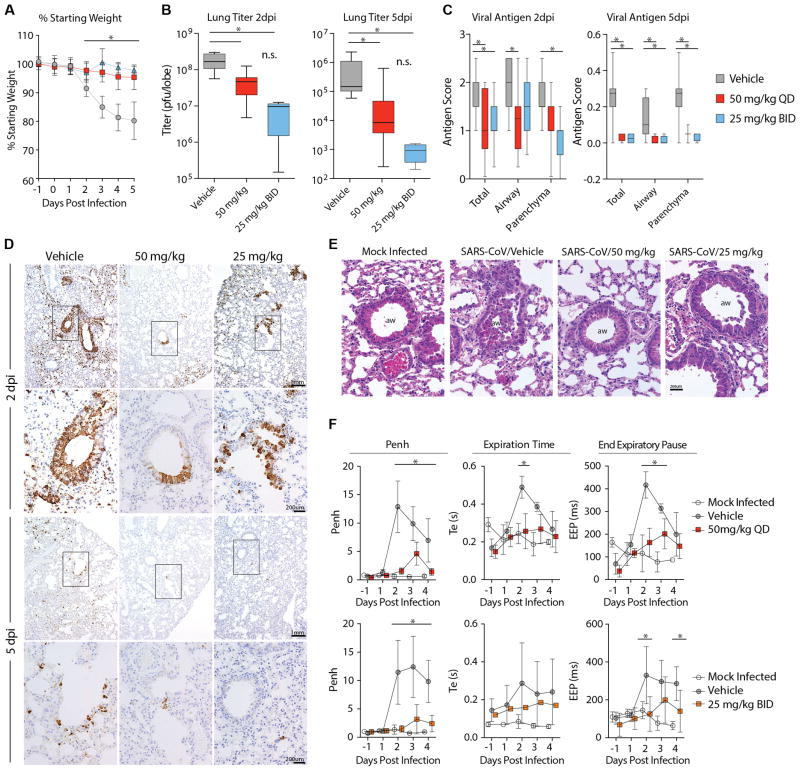
Figure 5. Prophylactic treatment with GS-5734 reduces SARS-CoV disease.
(A) Percent starting weight of Ces1c−/− mice infected with 104 pfu SARS-CoV MA15 treated beginning -1dpi with either vehicle (n = 42), 25mg/kg twice daily (BID, n = 25) or 50mg/kg once daily (QD, n = 28) GS-5734. (B) SARS-CoV lung titer in panel A mice at 2dpi (left) (Vehicle N = 11, 50mg/kg N = 11, 25mg/kg N = 5) or 5dpi (right) (Vehicle N = 13, 50mg/kg N = 13, 25mg/kg N = 4). (C) Quantitation of SARS-CoV antigen in lung sections in panel A mice at 2dpi (left) (Vehicle N = 15, 50mg/kg N = 12, 25mg/kg N = 7) or 5dpi (right) (Vehicle N = 10, 50mg/kg N = 12, 25mg/kg N = 4). (D) Photomicrographs of SARS-CoV antigen staining (brown) and nuclei (blue) in lung sections from 2 and 5 dpi. (E) Photomicrographs of hematoxylin and eosin stained mouse lung sections from 2dpi highlighting the conducting airway lumen (aw). (F) Whole-body plethysmography (WBP) to measure pulmonary function in panel A mice. Penh is a surrogate measure of bronchoconstriction. Expiration time is the time taken to release one breath. End of expiratory pause is the time between breaths. Symbols and error bars for panels A, B, D, and I represent the mean and standard deviation. The boxes encompass the 25–75th percentile while the whiskers represent the range in C, E and F. Asterisk indicates statistical significance (p<0.05) by two-way ANOVA with Tukey’s multiple comparison test for D, F, and I and Kruskal-Wallis in E.