Figure 2.
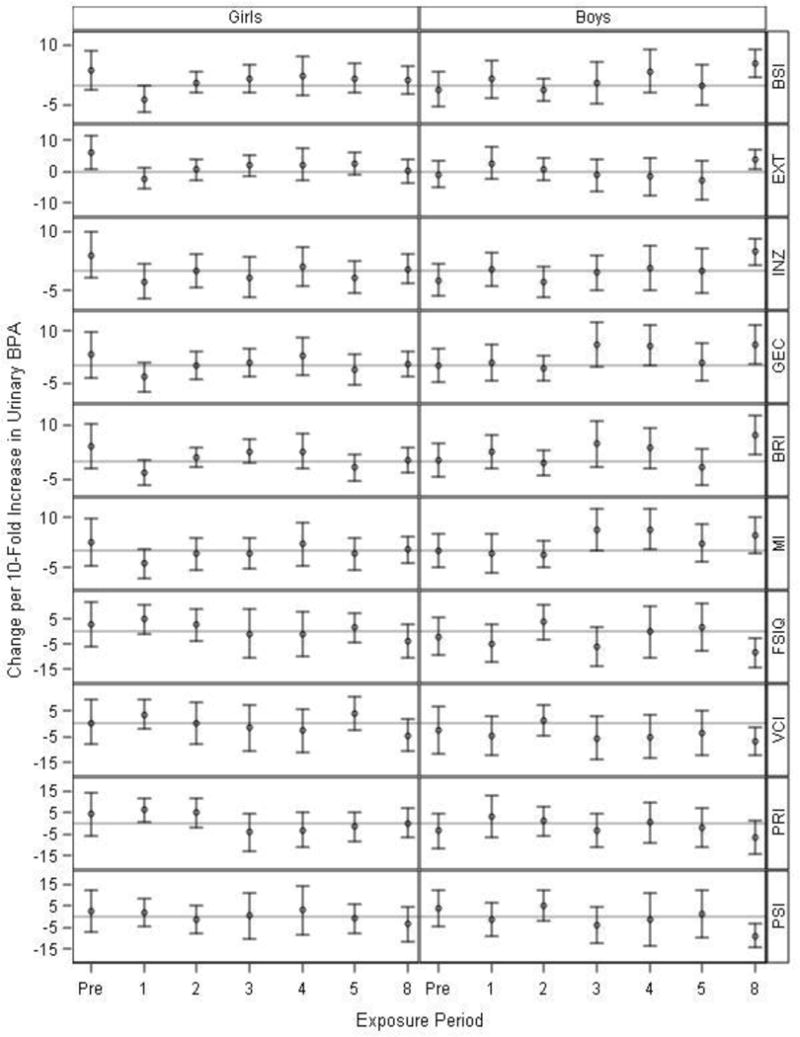
Adjusted1 difference in BASC-2,1 BRIEF,1 and WISC-IV2 IV scores at 8 years of age with 10-fold increases in prenatal and childhood creatinine-standardized urinary BPA concentrations, in girls (N=72–117) and boys (N=59–93).
1Adjusted for: visit, BPA × visit, child’s sex × visit, BPA × child’s sex, BPA × visit × child’s sex, child’s race, mother’s education, household income, caregiving environment, marital status, prenatal serum cotinine concentrations, prenatal vitamins, mother’s BDI, and mother’s CAARS.
2Adjusted for: visit, BPA × visit, child’s sex × visit, BPA × child’s sex, BPA × visit × child’s sex, child’s race, mother’s education, household income, caregiving environment, marital status, prenatal serum cotinine concentrations, prenatal vitamins, and mother’s full-scale IQ.
BPA × visit × sex interaction term p-values were 0.05, 0.02, 0.23, and 0.17 for the BSI, EXT, INZ, and BRI, respectively, indicating differences in time windows of BPA exposure between girls and boys. Heterogeneity p-values were >0.2 for all other outcomes. Exact sample sizes at each visit are available in Supplemental Table S5.
Higher BASC-2 and BRIEF scores indicate worse behavior or executive function, while higher WISC-IV scores indicate better cognitive abilities.
Abbreviations: Pre=Prenatal, BASC-2=Behavioral Assessment for Children-2, BRIEF=Behavior Rating Inventory of Executive Function, WISC-IV=Wechsler Intelligence Scale for Children-IV, BSI=Behavioral Symptom Index, EXT=Externalizing Problems, INZ=Internalizing Problems, GEC=Global Executive Composite, BRI=Behavioral Regulation Index, MI=Metacognition Index, FSIQ=Full-Scale IQ, VCI=Verbal Comprehension Index, PRI=Perceptual Reasoning Index, PSI=Processing Speed Index, BDI=Beck Depression Inventory, CAARS= Conners’ Adult ADHD Rating Scale
