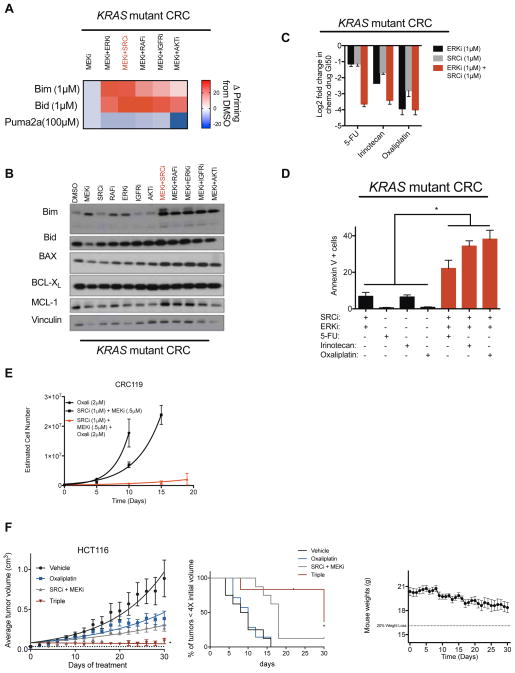
Figure 5. Leveraging the priming ability of two-body combinations to design triple combination therapies involving cytotoxic chemotherapies.
A) BH3 profiling in the KRAS mutant CRC cell line HCT116 treated with the indicated combinations (MEKi AZD6244, 1μM; RAFi LY3009120, 0.5μM; IGFRi GSK1838705A, 3μM; SRCi dasatinib, 0.5μM; ERKi SCH772984, 0.25μM; AKTi MK2206, 5μM). B) Immunoblot of indicated proteins in CRC119 CRC cell line treated with the indicated combinations (Drug identities same as above with following doses: MEKi 1μM; RAFi 0.2μM; IGFRi 1μM; SRCi 0.5μM; ERKi 0.1; AKTi 5μM). Blots are cropped for clarity. C) Log2 transformed GI50 values for three separate cytotoxic chemotherapeutic drugs treated with either vehicle or a constant background dose of an ERKi (VX-11e), a SRCi (dasatinib), or the combination of both. D) Apoptosis measurements reported as percent annexin V+ cells treated with the indicated drugs for 48hrs in CRC240 cells. SRCi (dasatinib 100nM), ERKi (VX-11e 500nM), 5-FU (5μM), irinotecan (5μM), oxaliplatin (5μM). E) TTP in CRC119 cells treated with the indicated drugs. SRCi (dasatinib), MEKi (AZD6244). F) HCT116 xenograft treated with vehicle, Oxaliplatin (7.5 mg/kg once every 4 days), dasatinib (15 mg/kg, daily) and AZD6244 (10 mg/kg, twice daily), or the triple combination. To the right, a survival curve showing percent of mice with tumors less than 4X the starting volume at a given time. To the right of survival curves, mouse weights for the triple combination group over the course of the study. Error bars show data ± SEM. *p<0.05. See also Figure S5.