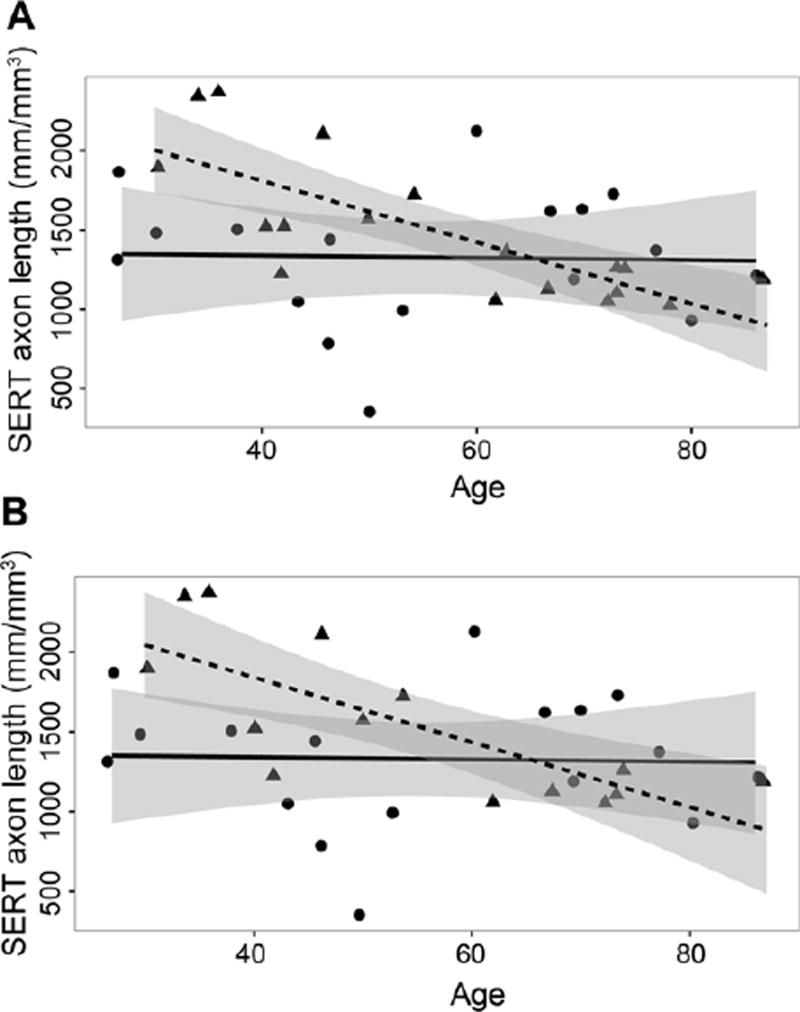
Figure 2.
Correlation between age and serotonin transporter (SERT)-immunoreactive (ir) axon length in layer VI of the orbitofrontal cortex for control and depressed subjects. A) all control subjects (circles, N=17) and all subjects with major depressive disorder (MDD, triangles, N=18), and B) all control subjects (circles, N=17) and subjects with MDD without an antidepressant drug in postmortem toxicology (triangles, N=14). For (A), there was a significant negative correlation (r= −0.77, p<0.0005) between SERT-ir axon length and age in MDD; there was no significant correlation (r= 0.03, p>0.05) between SERT-ir axon length density and age in control subjects. For (B), there was a significant negative correlation (r= −0.76, p<0.001) between SERT-ir axon length density and age in MDD; there was no significant correlation (r= 0.03, p>0.05) between SERT-ir axon length density and age in control subjects. Regression lines for control subjects are solid and those for MDD subjects are dashed. The 95 percent confidence intervals for the regression lines are shaded gray.