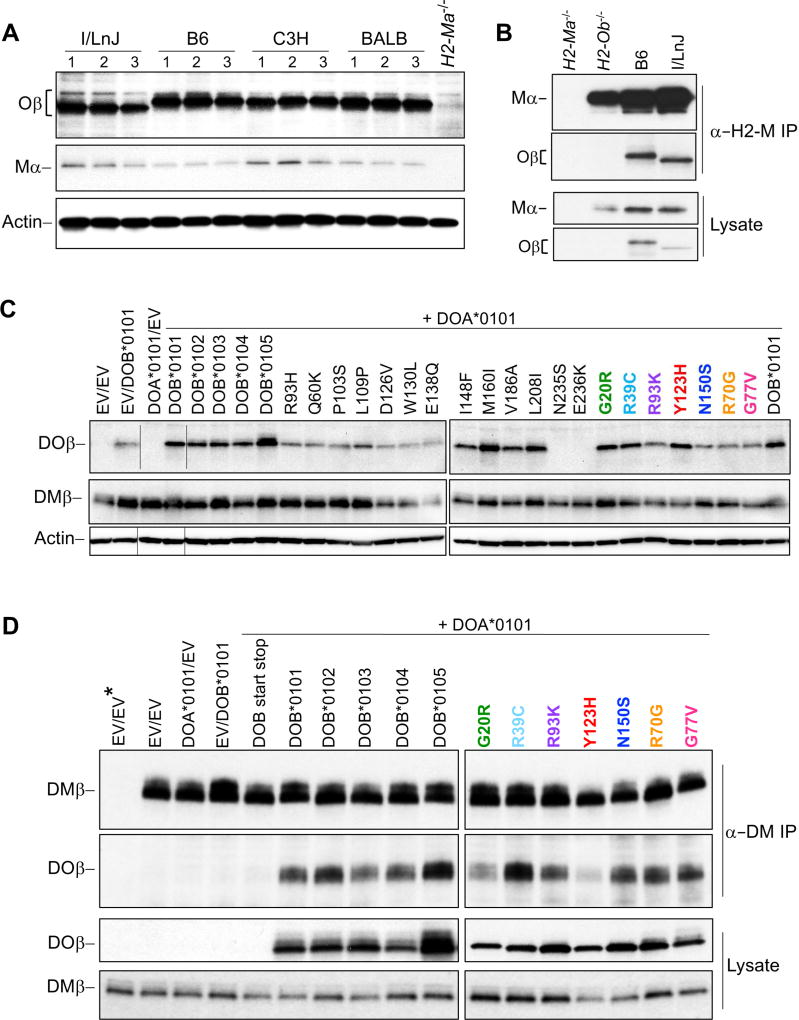
Figure 7. Human and I/LnJ Ob/DOB alleles interact with H2-M/DM.
(A) Oβ and Mα protein levels. B cell lysates from the indicated mouse strains were probed with Oβ luminal domain (top), Mα luminal domain (middle), or β-actin (loading control; bottom) specific antibodies. Purified H2-Ma−/− B cells were used as a negative control. Quantitation of protein levels for multiple mice are shown in Figure S7A. Note that the faster migration of I/LnJ Oβ on SDS-PAGE was restored after electrophoresis in the presence of 8M urea indicating that the observed aberrant migration was likely due to amino acid substitutions in I/LnJ that resulted in more SDS binding and not due to protein truncation (Figures S7B and S7C).
(B) H2-O and H2-M are associated in I/LnJ B cells. H2-M captured from lysates of purified B6, I/LnJ, H2-Ob−/− or H2-Ma−/− splenic B cells was analyzed by western blotting with Abs specific for Mα or for the Oβ luminal domain (top). Western blotting of lysates used for the immunoprecipitations are included as controls (bottom). Data are representative of 4 similar experiments.
(C) Conformation of DOβ variant protein expression by western blot analysis. Whole cell lysates from HeLa.CIITA cells transiently transfected with plasmids expressing HLA-DOA*0101 and the individual HLA-DOB variants (as indicated) were probed with polyclonal serum to the cytoplasmic tails of DOβ (top) or DMα (middle) or to α-actin as a control. Cells transfected with empty vectors (EV) or with HLA-DOA*0101 plus EV or HLA-DOB*0101 plus EV were included as controls. Data are representative of 4–5 similar experiments. The DOβ N235S and E236K variants have cytoplasmic tail missense mutations that abrogate recognition by the DOβ tail specific sera. Lanes (indicated by horizontal lines) in the DOβ and actin blots were spliced to present data in a logical order.
(D) All but one DOβ variant with altered function produced DO proteins that interacted with DM. DM captured from lysates of HeLa.CIITA cells transfected with plasmids encoding HLA-DOA*0101 and the seven HLA-DOB variants with altered function, with the five common alleles (positive controls) or with negative control plasmids was probed by western blotting with Abs specific for the cytoplasmic tails of DMβ or DOβ (top blots). Western blot analyses of lysates used for the immunoprecipitations are included (bottom). Data are representative of 3 similar experiments. DOB alleles with altered activity are color coded as in Figure 6. Empty vector; EV, *; indicates immunoprecipitation performed with mouse IgG as a negative control.