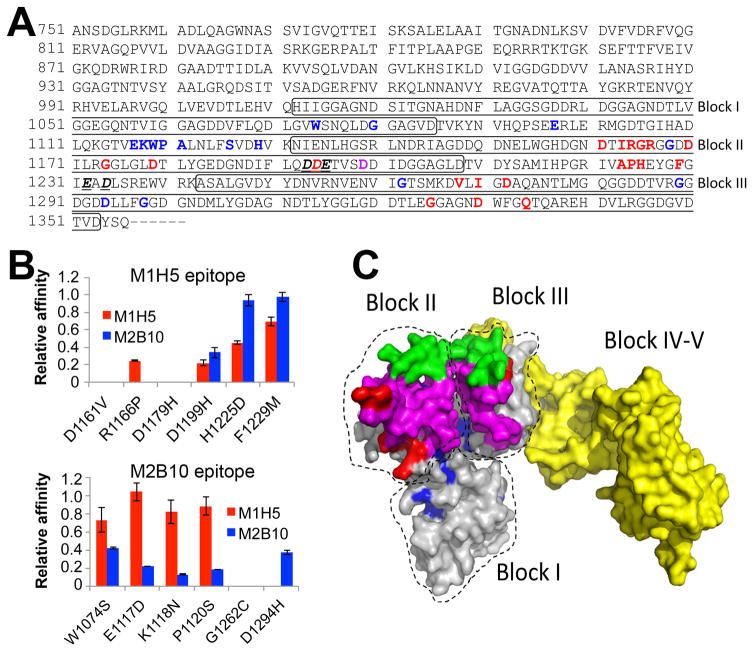
Figure 8. Antibody epitope residues on RTX751 identified by next-generation sequencing.
A, The RTX region subjected to random mutagenesis is shown. Bold and red letters indicate candidate M1H5 epitope residues, while bold and blue letters identify potential M2B10 epitope residues. The sole shared residue is indicated by bold and purple. Bold, underlined and italized residues indicate those implicated in receptor binding 30. The boxes indicate the first three Gly-Asp rich repeat blocks. B, Six residues identified as potentially participating in each antibody epitope were individually altered to the most common enriched amino acid residues observed after sequencing of sorted libraries. Each variant, with a single residue change, was expressed and purified as soluble RTX751 protein. Binding affinity of M1H5 and M2B10 monovalent scAbs for each of the RTX751 variants was assessed by ELISA. Data is represented as relative affinity (EC50,wild-type/EC50,variant), so that a lower value indicates reduced binding. C, A predicted structure of RTX751 was generated using the RaptorX web server44 and the experimental structure of domain V (PDB 5CVW or 5CXL). Residues 1015–1679 encompassing the five repeat blocks are shown, with the individual block locations indicated. The putative epitope residues are highlighted in red for M1H5 and in blue for M2B10, the block II variable region is shown in green, the putative receptor binding site is shown in magenta and the block IV–V region in yellow.